Ismétlés: Nem rokonokat keresünk, csak a magyar vándor nyomait!
Amerika 13
A kontinens és Óceánia.
Északon
CALIFORNIA PLACE NAMES OF INDIAN ORIGIN: A. L. KROEBER
Amerind California Kalocsa, Madocsa
There are nine counties in California, Colusa, Modoc, Mono, Napa, Shasta, Tehama, Tuolumne, Yolo, and Yuba, whose names are demonstrably or almost
demonstrably of Indian origin, and two others, Inyo and Siskiyou, that presumably are also Indian. Colusa. "The Shell Indians". Colusa means "fierce people," and they were described as a fierce, war-like people. Településeikből: Tavaguemue, Tampa, Sinapa, Sacaspada, Guarungunve, Estame..
Kato, for an Athabascan tribe or division, but is a Pomo word, meaning "lake".
Chumash Kayiwlish, "my head". Cayuca, a form of the name that also appears, denotes "head" in Cuban Spanish.
"Mussel" (kagyló) is khal, hal, in Northern Pomo.
Catacula, in Napa County, is a name of unknown origin.
Colusa County is named from the Patwin, that is, Southern Wintun, Koru, a village on the site of the present town of Colusa. (Colucha?)
Wintun ketten or hetten, "cammas" - edible root.
Inaja, more properly Inyaja, an Indian reservation in San Diego County, is named from Dieguenyo Indian Any-aha, "my water." (Enyém inni?)
Kuna Peak, between Tuolumne and Mono counties, is probably named from the Shoshonean word kuna, usually meaning "fire" but appearing in the Mono dialect of the vicinity with the signification of "fire-wood".
Mohave (Not Mohawk!), from Hamak-hava. Three is hamok in Mohave. "Havi" jelent "hegy"-et is. Azért tán nem "hármashalom".. A szó hasonlít a quechua "xamakxáv" szóra. A mohave nyelv a "yuman". Mohave nyelven a Nap=Anya és a Hold=Haly'a.
Napa County and City are said by Maslin and others to be named from an Indian word meaning "fish". Shoshonean "pala = water".
"Tulu-kai" or Tuluka, meaning "red," a Southern Wintun or Patwin village near the State Hospital at Napa.
Ores, "bear", and uri, uli, "head, hair, or forehead", are the only Costanoan words.
Hétváros These were the "Seven Cities of Cibola" which Gallatin, Squier, Whipple, and others have contended were near Zuñi. On the contrary Emory and Abert of the United States Army have conjectured that Cibolletta, Moquino, Pojnati, Covero, Acoma, Laguna, and Poblacon, a group of villages some ninety miles east of Zuñi, furnish the site of the seven cities. /Spanyol eredetű: siudat (siudatnan) = city - Spanish, ciudad; Portuguese, cidade./
Napo
In Comorian (Shikomor), by Najib : mwezi = moon. This language is spoken in the Comoros Islands

Camore: Területnév. Mint komor bikáé, olyan a járása. Arabic word "qamar =moon". sycamore: fügefa, eperfa, szederfa, hegyi juhar a különböző fordításokban. Az érett füge színe purple. Lehet, hogy innét jött a "sycamor" ? Purple: Spanish: morado; Malay: ungu. In Mardin, the word mor, meaning purple, does not only refer to a color. In fact, "mor" also means saint. A Comore szigeteken is van Missouiri település. Morocco területén Missour. (Outat El Hajj/Missour ) Talán missouri (sziú) indián misszionáriusok adták a neveket? Ngazidja Comorian: "madji=water". Ndali: "mishi=víz". Ojibwe: "ziibi=river". Vajon a "sycamor" az Hold szín (sy-camor), vagy "lila kéz" (sica-mor) ? Miriam "keze": Arabic: "Kef" Miryam. A tuaregek kék színe az indigó festéktől lehet, s amikor belenyalnak, a szájuk is megkékül.
Υ Pronounced in Modern Greek [i], this was [u] in Doric and [y] in
Attic. The reflex of this phoneme in Tsakonian is [u], and [ju] after coronals (suggesting an origin in [y]). σούκα [ˈsuka] corresponding to Modern σύκα [ˈsika] "figs", άρτουμα [ˈartuma] corresponding to άρτυμα [ˈartima] "bread"; λύκος
[ˈlykos] > λιούκο [ˈljuko] [ˈʎuko] "wolf" (forrás: wiki)
Arapaho hangváltás - s > n.
siipiiwi (river) > Arapaho níícíí. Ojibwe: ziibi. Rokonságban: Ankwe (West Chadic) sip ‘river’.
Ojibwe
Potawatomi (pot) is a language spoken in the Great Lakes region and Kansas in North America. It is spoken by the Potawatomi, who call themselves the Bodéwadmi, which means Keepers of the Fire.
Potawatomi Dictionary
bald eagle= beshkno. dance= nimedi. father= os. fire= shkote'. girl= gigyago; girls= gigyago-yuk. glove= mcenkawen; gloves= mcenkawnak. grub worm= mosik. he died= emboweg. king= ogama. make the fire= bodwe'n. Ottawa= Tawak. river= sibe. star= nagos; stars= nagosuk. /Potawatomi (also spelled Pottawatomie; in Potawatomi Bodéwadmimwen or Bodéwadmi Zheshmowen or Neshnabémwen) is a Central Algonquian language and is spoken around the Great Lakes in Michigan and Wisconsin, as well as in Kansas in the United States, and in southern Ontario in Canada, by 9 Potawatomi people, all elderly./
Ottawa - Öt tava: Felső-tó, Michigan-tó, Huron-tó, Erie-tó, Ontario-tó. Persze, a város kissé távolabb van a tavaktól, a Madawaska föld elválasztja tőlük. (Van másik!) Magán az Ottawa folyón (Kichissippi= Algonquin word for Great River) is található 5 nagyobb tó az atlasz szerint, azonban műholdról nézve az "ezer tó országa" a vidék.
Etymology: From English Ottawa, ultimately from Ojibwe odaawaa ("traders": Animate plurals end in –g, which inanimate plural nouns (and obviative nouns) end in –n. ). Itt a Kichi-ssippi "Nagy folyó". Kicsi módosulattal: The name Missi-ssippi is possibly based on the Chippewa Indian words "mici zibi" meaning "great river". Chippewa/Ojibwe: Bad River- Mashkii-ziibing. River/Folyó- Ziibi. Sun/Nap- Giizis. Moon(s)- Dibiki-giizis(oog)/éjszakai nap(-ok). /Hurrian "Zi-ib-bi" and Akkad "Zibü" toponym means "black cumin". Fekete kömény./
Még szavak: Mishi-makwa = Great Bear. Ugh = yes/Igen. Me'da = a medicine-man. Water (Víz) = Nibi. /Nipigon tó!/ Állítólag a modernebb "kichi, gichi" nem "kicsi", hanem épp úgy "nagy" jelentésű, mint a "Michi". A "kicsi=bangii" lenne.. Small = agaasaa. Mizar: Nem a NAGY urak folyója. Missouri River, which was named after the indigenous Missouri Indians, a Siouan-language tribe. A Missouri neve pedig "fahajó" lehetne, de a felső folyása felett Souris folyó és a "souris=egér" a francia gyarmatosítóknál. Miből a Missouri az "nagy egér" netán "faegér" lehetne. (Mih=fa/wood). Dakota szavak: "minne = water". maza = metal. "maka ina=föld anya". APACS: "besh=metal". Gusano=you worm. Holos=Sun. tu=water.
A Souris partján fekszik Estevan település, mely nevét állítólag George Stephen vasúti elnök után kapta spanyolosítva. Saskatchewan capital: Regina. Cree Indian word kisiskatchewanisipi, which means "swift-flowing river," and was first used to describe the Saskatchewan River. Egy részletesebb kifejtése a Missouri szónak. Különben a Kirkwood székhelyű "The Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod (LCMS)" az egyik legnagyobb felekezet az USA-ban. Magyarországon pedig gyakori családnév a "Miszori", legalább is az utóbbi időkben. Luo nyelven "Hogy vagy?" Habari? válasz: Misori Jól.
OROKO NAMES: Misodi or Misori and Bekeli (tears). Mokori (hill) > Finska - mäki (hill).
Kenyában viszont ilyen nevek vannak, mint: Mihoro, Migori, Misori..
Mysore state in southern India. Sanskrit Mahisha means buffalo.
Ad-vesz
Odaawaa (syncoped as Daawaa, supposedly from the Anishinaabe word adaawe, meaning "to trade", or "to buy and sell") is a term common to the Cree, Algonquin, Nipissing, Montagnais, Odawa, and Ojibwe.
Three Fires as well. In addition, the Ojibwa are the "keepers of the faith," the Odawa are the "keepers of trade," and the Potawatomi are the designated "keepers/maintainers of/for the fire" (boodawaadam).
Sioux - Saami
A sacred mountain named Haldi, which rests among a group of mountains near Alta and an 814 meter-tall conical sacred hill named Tunnsjöguden in central Norway are examples. In general, the word saivu is applied to sacred mountains in the South while the terms bassi, ailigas and haldi are used for sacred mountains by Northern Sami.
Vagy a lappok vitték kultúrájukat amerind földre, vagy az indiánok hódították meg laplandot. Esetleg egy harmadik nép járt mindkét helyen..
Dakota és Sioux nyelvek altáji kapcsolata
So far as we know, the Dakota language, with several cognate tongues, constitutes a separate class or ftunily among American Indian languages, of which we may speak on some other occasion.
Dakota nyelv
HINTO: Baby name books say that this name means "blue" in Dakota Sioux. Actually, it means "blue hair." If you've got a blue roan horse or something, it might be a good name for it. For a child, it would be rather odd.
HONOVI: This one is claimed to mean "strong" or "strong deer" in Hopi. Probably this originally came from a typo. Hopi for "strong" is "hongvi," and some baby book author who knows nothing about the language probably misread the 'g' as an 'o' at some point. The "deer" part is just an Anglo embellishment. Dakota szavak.. Forrás víz: Spring, water: Wee-wee lah.
Mandan is an endangered Siouan language. American Indian people of the Missouri River valley in North Dakota.That Mandan is not Welsh: There is a common myth that the Mandan people of North Dakota are in fact the decendants of Welsh colonists who sailed form Wales under Prince Madog. Azért a "ház" szavuk hasonló: "ty = ti = house". A tűz helye (hearth)..
Nor does the fact that the Mohawk pronominal affixes for 1st and 2nd person—/k/ and /s/— match the Hungarian affixes make it reasonable that the early Iroquois settled Hungary. These sorts of similarities are bound to happen. Historically, Mandan ‘ti’ would be related to /tipi/ in Dakota, while Welsh ‘ty’ is derived from Indo-European *tegos meaning cover/roof (English thatch). So these two words, although superficially the same, stem from different sources. Nyelvükben a "Hold=Itun Minaki". Az IE *tegos rokona lehet a magyaros TETŐ-keresőknek. Tectosages..
Joseph
Harold Greenberg: Language in the Americas
FOOT: Atanque: kosa; Atacama: Kh'oche; Kagaba: kasa. (Foot=láb. > vándor - kósza - kocsi.)
FEATHER: Bintucua: kui; Murire: ga; Yupultepec: kaya. Gayon: besa. /Koreából "Shilla > toll, kő, fehér.."/
EYE: Atacama: kepi; Cayapa: kapu-kua; Moguex: kap. (Máshol a "kap=kéz" és a "kep=kert, őriz". A magyar KÉP kapcsolható a szemhez.)
EARTH: Allentiac: tawe; Colorado: to; Chimila: iti. (Earth=Föld. Egyéb nyelvekben a "tó=lake". Mohawk "itun=otthon"?)
HAND: Manare: kus-kara; Nortenyo: kuse; Paez: kus. (Itt pedig a finn rokonság. Kéz= käsi.)
RIVER: Chimila: koono; Paez: "kina=canal".
URINE: Kagaba: wisi; Miskito: is(-ka); Borunca: wis(-ku). (Urine=pisi. Az "élet" vize.)
VAGINA: Bintucua: sisi; Cuna: sisi; Cayapa: su. (Rokonságban: si, ci, haluna..)
Kay (tagalog):
Naroon kay Tina ang gamit mo. = Your stuff is with Tina.
Umalis siya kina Mrs. Santos. = He left (from) Mrs. Santos' place.
Binili ko ang bulaklak para kay Ida. = I bought the flowers for Ida.
kay Mariang kapatid = Maria's brother.
Philip Briggs: There are two types ofwat sauce: kai wat is red in colour (kai literally means red) and very hot, and flavoured with beriberi (peppers). In the Amharic language, the word "kai" means "red".
"Klee Kai" even means "small dog" in Alaskan Athabaskan language. Kai means 'ocean' in Hawaiian and 'rejoice' in Finnish. Toward the ocean: Ma kai – "mah ky-ee" .
Fijian dict: kai = people. Thai: 'Gai' means chicken while 'kai' means egg.
Muskokee indián: "hesh=see/néz". Yuki indián "häl=hear/hall". Tunica "laka=live/él,lakik". Maya "laq=dwell/lakik".
Duit nyelven "oba=nagy". Afrikában "oba=király". Sinsiga: "uba=star".
Atacama nyelv: "kabur=high hill". Arab: "nagy=kabir".
Indián nyelvek
COVER: Karok nyelv: "sap=close"; Mohave: "sapet=close"; Yurumangui: "sipa-na=hat". Sapka szavunk eredete? "Takar" változat?
FULL: Quapaw: "pana=all" > greek "panacea"?
HAND: Caddo: sik; Andaqui: saka-a; Chibcha: yta-saka.
Unami "nemesek": Lenape noun plural mark: -k; names = hal; namesak = halak
Lenape glossary (Delaware) and dictionary
feathers mikwemak. Similar "mikmak", but "-ak" is plural mark.
hus ['hus] bucket n.a.
hus-ak ['husɐk] bucket-s.
nipen = summer.
nipahum = moon.
|
frogs chakolak. (chakonika, the language of ancient Sparta "frog=bukaka")
wik- = dwell. Nem öböl. Mint a latin Vicus. Vicinalis. Helyi érdekű.
wik-ewam = house. Wigwam. (compare modern Dutch 'wijk=hamlet')
wil = head.
zit = foot. (balti "zsid")
newa = (4) four. Más nyelveken "víz". |
Szép képek: Kígyódomb északon és Machu Picchu délen.
Micmac
The Micmacs' neighbors recognized their territory and rarely violated its borders. Micmac people thought of their homeland as containing seven districts: Kespukwitk, Sikepne'katik, Eski'kewaq, Unama'kik, Piktuk aqq Epekwitk, Sikniktewaq, and Kespe'kewaq. A keptan orsaqmaw (district chief) presided in each jurisdiction, doubling as local ruler and delegate to the Grand Council Sante' Mawiomi.
A sós víz leszármazottai: - Sóurak magnak hagyva?
A parti népeket Bakker és társai meggyanusították baszk szóátvételekkel. Mindenesetre a micmac népnél feltűnik a szent koronánk indián változata, mint sámánkorona. A Micmac nyelv nem szereti az "r" hangot, helyette "l"-t használ. Pl a törzsfő/király az "elege", míg a baszk nyelvben "errege", aminek bizonyára köze sincs a regolith-hoz vagy a régenshez. Seboo: = A river. (A large river was a "ukcheseeboo.") ..régmúlt dicsőségről regél..
Keserűsó: Salt. Cognate with gazi. Outside of basque, cf. mongolian gasi- "bitter", amerind (quechua) katchi "salt".
Francia kapcsolat: In 1606, for example, the Souriquois (Souri-s river?) under the leadership of Membertou raided other Indian villages using sailing shallops. The following year, the English on their way to establish their colony on the Kennebec River encountered two sailing shallops being used by Souriquois (salt water man) under the leadership of Membertou. The Souriquois offered skins for trade and the English noted that the Indians seemed to be using a lot of French words. The Micmac called their land Megumaage and may have called themselves So-ur-iquois.
Irokéz: Algonquian Irinakhoiw, literally, 'real adders'. A mohikán is "kígyó" nép. Nadene m csak az! Kalmyk kígyó: Moha. Iroquois katno aiss’ vizmi (cuts no ice). -quois=(pl mark) > Ir-k?
Basque-Algonquian pidgin h)irokoa 'killer people', from Basque ((h)ilo 'kill'+ koa 'person'. (http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/) Ilo-cano?
Iroquois via French < late medieval Basque *erukoak, irukoak ‘Irishmen’; The Etymology of Iroquois: "Killer People" in a Basque-Algonquian Pidgin or an Echo of Norse Irland it mikla "Greater Ireland"?’ Onomastica Canadiana 88 (2006): 43-56.
Helynevek - etimológiai próbálkozások
Lenni-Le-Nape "Real men" or "original men" - the name the Delaware Native Americans called themselves. Three sub-tribes included the Munsee (wolf), Unami (turtle), and Unalachtigo (turkey).
Manayunk "Where we go to drink" - Delaware name for the Schuylkill River.
Minnequa Town in Bradford County, Pa., from the Delaware Menan, meaning "to drink"
Messze Jeruzsálemtól - nemec
Maku (Macu, Máku, Mácu, Makú, Macú) or Maco (Mako, Máko, Macó, Makó) is a pejorative term referring to several hunter-gatherer peoples of the upper Amazon, derived from an Arawakan term ma-aku "do not speak / without speech". Más nyelvből: Gyermek jelentésű.
the "Wirö" dialect nem azonos a vöro dialektussal a Balti környékéről.
Hup nép
The Hupd'äh people live in the region bordered by the rivers Tiquié and Papuri, tributaries that join the left hand bank of the river Uaupes in the Upper Rio Negro region of the state of Amazonas in Brazil.
The Kakwa people live on the streams on the left hand side of the Papuri River, in Colombia, and maintain sporadic contact with the Hupda who live on the streams flowing into the Papuri River.
Paprika szavunk a Távol-Keleten "papurika".
The word Maku is not Hup. It probably comes from the Arawak (Baniwa) and means "he who does not have language" or "he who does not have our language". Makog?
Elm tree - mintha a tudás, rejtőzködés szavakhoz kapcsolódna.
Hungarian: szil
Cherokee: dawatsila
Estonian: Künnapuu
Apache
Most Apache people lived in wickiups, which are simple wooden frames covered by a matting of brush and sometimes a buffalo-hide tarp. Wickiups were small dwellings, often the size of a modern camp tent, and an Apache woman could build a new wickiup in two hours if there was enough brush available. Here are some pictures of Indian brush houses. The Plains Apaches and some Lipan Apaches used buffalo-hide tipis as housing instead, which are more spacious and easier to heat than wickiups.
Messze tornyokat látogat sorba.. - "Hopi őrtorony".
Indian Watchtower at Desert View, is a 70-foot (21 m)-high stone building located on the South Rim of the Grand Canyon within Grand Canyon National Park in Arizona, United States. The tower is located at Desert View, more than 20 miles (32 km) to the east of the main developed area at Grand Canyon Village, toward the east entrance to the park.
Desert View: As Virginia L. Grattan wrote in Mary Colter Builder Upon the Red Earth, "The Indian watchtower at Desert View was not a copy, but what Colter called a 're-creation' of an Indian watchtower."
Zuni
Apache (probably from ápachu, 'enemy,' the Zuni name for the Navaho, who were designated "Apaches de Nabaju" by the early Spaniards in New Mexico). A number of tribes forming the most southerly group of the Athapascan family. The name has been applied also to some unrelated Yuman tribes, as the Apache Mohave (Yavapai) and Apache Yuma.
Sirenik - eszkimoföld
 A szibériai nyelvekhez hasonlóan a kettős szám jele a "-k", a többes számé pedig a "-t". Lándzsa = pana-m. 2 lándzsa = pana-k. Több lándzsa pedig pana-t. A filippino lándzsa "sibat". Náluk a pana az "íj és a nyíl".
A szibériai nyelvekhez hasonlóan a kettős szám jele a "-k", a többes számé pedig a "-t". Lándzsa = pana-m. 2 lándzsa = pana-k. Több lándzsa pedig pana-t. A filippino lándzsa "sibat". Náluk a pana az "íj és a nyíl".
Inupiaq szótárban: pana=spear, two edged cutting tool; panapkaaq=tent (q,s); paniga=my daughter. > milluk=both breasts/mellek > miluk=milk. (A tej/milk a mellek/breast terméke.) Maleko, malaka..
Merrit Ruhlen mellbedobással.. Akad, aki -helyesen - a MI NYELVÜNK (nostratic) alapszavát is itt találja meg *mälgi "to suck the breast", csak bizonyára félreolvasta kissé.
kaaksiubun=famine (N). kia=whose? kuyaaq=keel. igniq=fire (latin rokon?! igni, agni, égni, ugni). "igniruq=make fire with flint". igurvik=temporal/halánték. (Ott lakik az isten?) "ii=yes/igen". imiqabvik=water container with cover. ipi=handle (of a bucket etc.) > ipibautaq=axe. nafirvik=hospital (lit. place for sick ones). narvaq=lake. nipiruq=(sun, moon) sets > nippivik=November (lit. sunset time). niviaqsiaq=young lady (marriageable). sieigvik=bed (lit. sleeping place). suluk=wing feather. tanik=white person. tatqiq=month (moon). punnilivik=oven, (lit. bread-making-place). augavik=blood vessel. Más forrás
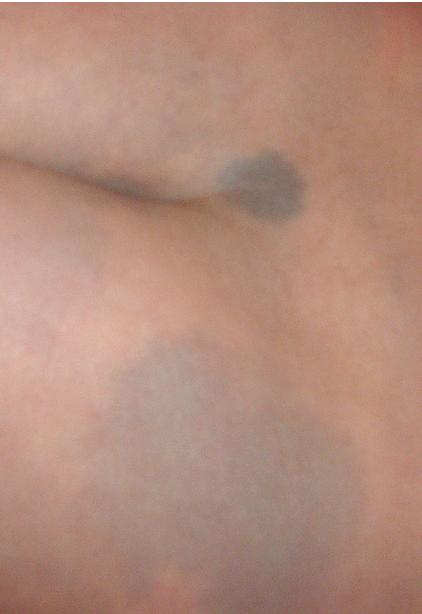
Mongol folt: Mongolian: menge; Korean: monggolban, "Mongoli Jeom"; Hawaiian: ila; Maori: ira; Inuktitun: sungauyaq (hungauyaq); Kalaallisut: annissaq; Itelmen: tixe-legen; Japanese: mouko han; (Spanish: rabo verde). German: Mongolenfleck ("Mongols' spot") / Sakralfleck ("sacral spot") / Steißfleck ("rump spot") / Hunnenmal ("Huns' mark"). Many Oriental and some Amerind babies, especially Maya, are born with the blue "Mongolian spot" at the base of their spine.
Mongolian spot. A szemita népeknél és a fehér emberekben ritka. Európában csak Hispania és a Kárpát-medence térségében található nagyobb arányban meg.
Indiánjaink. A másik etnikumunk orvosai szerint ez egyszerűen "cigányfolt", s hazánkban a romákon, a németeknél a török bevándorlókon tapasztalni. Amíg a törökök nem értek Németországba, addig "hun folt" volt a németeknél. Pedig szinti cigány akadt azért arra is!
Mezítlábasok?
Cressman found dozens of sandals below a layer of volcanic ash, subsequently determined to come from the eruption of the Mt. Mazama volcano 7500 years ago. Named for the site where they were first found, Fort Rock-style sandals have since been reported from ancient deposits in several Northern Great Basin caves.
Mezoamerika
Myth - az alvilág részei
House of Bats: Part of the Mayan underworld, Xibalba. Hunapu and Ixbalanque spent a night here and Hunapu's head was cut off by Camazotz.
House of Cold: Part of the Mayan underworld, Xibalba. Hunapu and Ixbalanque spent a night here and managed to survive.
House of Fire: Part of the Mayan underworld, Xibalba. Hunapu and Ixbalanque spent a night here and managed to survive.
Mexicoi csikó.
CHICO - Means "small" in Spanish, but it is also the nickname for the Spanish name "Francisco". In New Mexico "chico" is also identified with dried green corn. The Spanish words "chico rico" mean "rich little". Rico komancs nyelven madár.
Teotihuacan
Ix Chel maya
Taypikala (Tiahuanaco)
We know that Teotihuacan was built as a replica of how they saw the cosmos, the universe. We imagine the tunnel to be a recreation of the underworld.
Vizkaya
Nahuatl mítosz a Mexikó völgyeit lakó 7 törzsről. Mint látjuk, nem csak az írek mítoszában, vagy a perzsákéban szerepel a 7 törzs..
Maya hieroglyph
the suffix -kook in Algonquian usually means "river". Cancun - Mayan Word for Golden Snake. Can Cún az ottani maják nyelvén azt jelent, hogy "kígyófészek".
Aztec TL
Mayo: "kabba=egg". Tubar: "kova=egg". Nahuatl: "ka-kawa-tl=/cacao/ little egg".
*sutu-y "nail, claw; finger" > Nahuatl: iste, isti.
Maya - csolanba nem üt a mennykő
Mayan languages are the descendants of a proto-language called Proto-Mayan or, in K'iche' Maya, Nab'ee Maya' Tzij ("the old Maya Language").
As in other Mesoamerican languages, there is widespread metaphorical use of roots denoting body parts, particularly to form locatives and relational nouns such as Tzeltal/Tzotzil ti'na "door" (lit. "mouth of house"), or Kaqchikel chi ru-pam "inside" (lit. "mouth its-stomach").
Ch'olan languages are believed to be the most conservative in vocabulary and phonology, and are closely related to the language of the Classic-era inscriptions found in Central Lowlands. The Ch'olan languages were formerly widespread throughout the Maya area, but today the language with most speakers is Ch'ol, spoken by 130,000 in Chiapas. Its closest relative, the Chontal Maya language, is spoken by 55,000 in the state of Tabasco. Yucatan map.
The Maya site may formerly have been known by the name Zama, meaning City of Dawn (helyi nyelven: Hajnal. Testvérvárosa Kartago mellett), because it faces the sunrise. Tulum stands on a bluff facing east towards the Caribbean Sea. Tulúm is also the Yucatan Mayan word for fence, wall or trench, and the walls surrounding the site allowed the Tulum fort to be defended against invasions.
Lilly
 Pre-Columbian art
Pre-Columbian art
The Fleur-de-lis emblem ("flower of the lily") has long been a symbol of European monarchy and the sacred symbol of the Holy Trinity. Above, a painting of King Philippe II Augustus (1165-1223 C.E.), last King of the Franks and first King of France crowned with the Fleur de lis.
Perhaps not so surprisingly, the emblem of the Fleur de Lis in Olmec art and iconography carries the same symbolism as in the Old World, of rulership and divinity associated with a divine Trinity of creator gods, a Tree of Life and it's forbidden fruit, the so called mushroom of immortality.
The Fleur de lis symbol in the New World as I have discovered has the same meaning as in the Old World of a Trinity of creator gods associated with a World Tree or Tree of Life. The Maya ruler from Coba holds a "Double-headed-serpent-bar," also known as the Bicephalic ceremonial bar, which has been identified as a symbolic representation of the "World Tree", known among the ancient Maya as the Wakah Chan, meaning, Raised-Up-Sky, a sacred portal that leads to the supernatural world of immortality. Archaeologist Sylvanus G. Morley believed the Maya bicephalic serpent bar symbolized the highest religious rank during Classic times.
A maya szobron egyértelműen látszik, hogy a középső ág valójában egy fenyőtoboz. még toboz. De hasonlóak a Baphomet ábrázolások is. Azonban Dunhuang környékéről is figyelemre méltó a kereszt 2:30 időnél.
Gomba mítosz
Above on the left is a drawing of an Olmec stone celt (900-500 B.C) portraying a winged deity crowned with a Fleur de lis symbol. The drawing above is of Stela 20, at the archaeological site of Coba in Quintana Roo, Mexico, that portrays the accession of a Maya ruler crowned with a symbol similar in shape to the Fleur de lis. The Maya ruler is depicted impersonating the Maya god Chac-Xib-Chac. He holds a "Double-headed-serpent-bar," also known as the Bicephalic ceremonial bar, representing the "World Tree", known as the Wakah Chan, or Raised-Up-Sky, a sacred portal that leads to the supernatural world of immortality.
 Régi címerünkben jobban hasonlít az Ücs tepét az apostoli kereszttel összekötő kép a liliomra, mint egy koronára. Mai címerábrázolásunkban direkt hangsúlyozzák a korona képet. A margitszigeti és az egyik koreai korona is liliom-szerű formákkal van bekerítve. Vagy csak stilizált turul madár?
Régi címerünkben jobban hasonlít az Ücs tepét az apostoli kereszttel összekötő kép a liliomra, mint egy koronára. Mai címerábrázolásunkban direkt hangsúlyozzák a korona képet. A margitszigeti és az egyik koreai korona is liliom-szerű formákkal van bekerítve. Vagy csak stilizált turul madár?
Maya mítosz
Among the Quiche Maya, Venus in its form as the Morning Star, was called iqok'ij, meaning the "sunbringer" or "carrier of the sun or day."
A liliom minta Teotihuacan falfestményén is megmaradt egy horgas csőrű madár mellett ábrázolva.
Baphomet - szarva közt a tőgye.
Ez az "őrdög" leszbikus volt, vagy hermafrodita ? Mindenesetre 5 ágú csillagot használt.
"The Gnostics held that it composed the igneous body of the Holy Spirit ; and it was adored in the secret rites of the Sabbat or the Temple, under the hieroglyphic figure of Baphomet or the hermaphroditic goat of Mendes."
Kuna indiánok
KUNA
A kunák autonomiát kaptak, amit nyelvükön "Comarca" néven emlegetnek. Földjük a "Kuna Yala" (San Blas), Panama északkeleti partvidékén. Yala állítólag "föld, hegy" jelentésű. Matriarchatusban élnek, s a férj az anyós házába költözik. Zászlójukon már Hitler előtt horogkereszt volt.
A river the Kuna called Akwadi, or Rock River, (from the words awka and di, meaning "rock" and "river") became Río Agua, or Water River.
The word Mola in Kuna language Tule Gaya, means blouse or clothing. (Kuna gunya?)
Mor
The Kuna are known for their decorative art, known as molas.
In the Kuna language Mor means Mola, make means making, and tupu means island.
Guna Yala
By Act of June 4, 1870 of Colombia was created Shire Tulenega, which also included the present territory of the District Guna Yala, the various communities of the District of Wargandí as Mordi, and Sogubdi Asnadi, as well as the communities of the region of Madungandi as Tiuarsicuá, and communities Guna of Colombia, as Tanela and architecture. The land area of the Shire Tulenega stretching from the province of Colon coming to the Gulf of Urabá, Colombia.
The Kuna live in three politically autonomous comarcas or reservations in Panama, and in a few small villages in Colombia. Comarques is a traditional region or local administrative division found in parts of Spain, Portugal, Panama, Nicaragua, and Brazil. Comarca term is derived from the term marca, meaning a "march, mark", plus the prefix co- meaning "together, jointly". Madársereg? Együtt haladva? Marca: "jel, határvidék" spanyol nyelven.
Darien Gap - Kuna és embera indiánok földje
Travel is often by dugout canoe (piragua). On the Panamanian side, La Palma is the capital of the province and the main cultural centre.
Ultima Tulé
Kuna language, they call themselves Dule or Tule, meaning "people".
inna=chicha helyi nyelven (sörféle); "tule, dule=person, Kuna person"; tiwar, diwar=river; neka, nega=house; wisi=know. (German: wissen)
Kreol. Lakhely, kajüt.
Eske ou konn ale Ayiti? = Have you been to Haiti? (lit. "Do you know to go to Haiti?") Ay-iti?!
lakay /lakaj/ = (French) la cahutte /la kayt/= "the hut"; "house" (inkább csak kalyiba, de lakhely.)
lalin /lalin/= (French) la lune /la lyn/ ="moon"
oungan /uga/ = (Fon) houngan = voodoo priest.
moun /mun/ = (French) monde ="people/person" (Kissé eltér a german MOND-tól.)
Haiti Kreol online szótár. Nem vennék rá mérget!
Swadesh list: Többnyire spanyol, francia, angol torzított átvételek.
Quechua
Quechua
The Quechuas of Ecuador call themselves as well as their language Kichwa–Kichwas or Quichuas. In Colombia, the Kichwa-speaking group calls themselves the Ingas. Other Quechua speakers call themselves runakuna (Quechua for "people", in Junín and parts of Ancash, Peru: nunakuna; singular: runa or nuna).
Moon - Kecsua ferdítések
The indigenous people of the Andes refer to themselves as the ‘Runakuna’. In Quechua (the language of the Andes) the word ‘runa’ means ‘person’, and the addition of ‘kuna’ to a word makes the word plural. Állítólag ma már a régies "-kuna" többes szám jel helyett a spanyolos "-s" van használatban.
We are living in the age of the Runakuna, which is the age of the sun, and we are the children of the sun. Before there was the sun (Taytay Inti) there was the moon (Mamma Killa), and before the Runakuna there were the Machukuna, the children of the moon, the ‘Ancient Ones’ (‘Machu’ is Quechua for ‘ancient’). Machu Picchu (kecsua nyelven: Machu Pikchu, "Öreg csúcs")
Machu Picchu means "old bird" in the Quechua language, with machu meaning old, and picchu being bird. Lost Ancient Technology Of Peru And Bolivia szerző: Brien Foerster Bár a modern szótár szerint a "madár=pisku" a kecsuában, itt a fiatal madár "Huayna picchu".
Az Özönvíz
In Inca mythology, Viracocha destroyed the giants with a Great Flood, and two people repopulated the earth. Uniquely, they survived in sealed caves. See Unu Pachakuti. A cebuano nyelvben "deluge/özönvíz=lunop".
Tuscarora: nyatar ‘sea’, in relation to *na, 'water'. a'churi "eat", in relation to *it'io, "tooth".
Semitic Quechua
Quechua has just three vowels, a/i/u (though allophonic o/e are found in some dictionaries).
amaru =snake, sage; amaru =know, teach (Assyr.) "mar=snake" persian.
k'ayra (Quechua) frog - krur (Coptic) frog
punku (Quechua) door - brg (Coptic) be open
apu (Quechua) god, mountain lord - abu (Assyr.) father.
Chinese: ti=earth; Quechua: tiksimuyu=earth; Spanish: tierra=earth.
Erről a lapról még a NŐ szavunk:
Chinese: nü=woman; Quechua: nyusta=princess; Dutch: nuf=aloof girl; Greek: (gy)ne=woman; Latin: (femi)na=woman;French: nana=woman.
Bolivia
Férfinyelv, amely apáról fiúra száll.
Bolivia is one of the most endangered and diverse language areas in the world. Two different Language Hotspots are found in this area. Kallawaya is a secret mixed language spoken by a group of traditional itinerant healers that date back as such at least to the private retinue of the Inka in the early fifteenth century and is one of the southernmost remaining languages of this Hotspot.
Warau indians
Cherokee language = tsalagi; Cherokee Nation = tsalagiyi ayeli; ... door = galohisdi; door = galohisdii; door = sdudi; door = stew de; door (entrance) = stuti, galuhisti. Worm= gusano (Tuo, Juba).
Indián jelképek
symbols
Native American Indians were a deeply spiritual people and they communicated their history, thoughts, ideas and dreams from generation to generation through Symbols and Signs such as the Feathers symbol.
The feathers of birds were highly esteemed for adornment and symbols of status. However, owl feathers symbolized death or prophesy.
The meaning of the Moon symbol was the protector and guardian of the earth.
The meaning of the Raven symbol signifies that danger has passed and that good luck would follow.
The feathers of the Red-tailed Hawk are considered sacred to many Native Americans and, like the feathers of the Eagle, are sometimes used in religious ceremonies and rituals.
The Falcon symbol featured strongly in the Mississippian culture, along with the other Bird Man symbols. The Falcon was believed to be a supernatural deity who resided in the Upperworld with the spirits of the Sun, Moon and Stars. Falcon symbol, from the Mississippian culture have been found in burial sites that contained war axes, knives and other weapons.
Napszimbólum
Sun Symbol (also known as the Zia symbol)- The sun symbol often means "Earth Guardian in Day", and it can also represent Healing Energy. The sun symbol is also recognized as a giver of life, and a provider of warmth.
The symbol of a frog in native american terms often means renewal, fertility, and it can also mean the arrival of springtime.
Pictograms és egy video a petroglyph Amerikában.
Kalifornia - nyelvcsaládok
Uruk, Iroquois, Uruguay
All at once, saying the word Iroquois out loud, it struck me that I was basically saying the same word as Uruguay. Say the two words out loud for yourself to see how they are related. Within a moment, it hit me that both of these words appeared to contain the phonetic element Urok, which was once the phonetic spelling of Yurok - the name of a Native American tribe inhabiting Northern California.
It is interesting to note that the Yurok language is not a Hokan-Sioux language. It is related to Wiyot, and both of these are called Algic languages (relatives of Algonquian languages like Ojibway and Cree). On the east coast of the United States, the Algonquians and Iroquois were neighbors speaking unrelated languages. On the west coast, we have a similar situation with the Karuks speaking an Iroquoian-type language and the Yuroks speaking an Algonquian-type language.
Afrikából jöttek
Papiamento is a language derived from African and Portuguese languages with some influences from American Indian languages, English, Dutch and Spanish.
Papiamento vocabulary: "horkan = hurricane". Horka = gallows/akasztófa. Saya = skirt/szoknya. Lansa = spear/lándzsa. Pata = claw/karom. Parha = bird/madár. Palu = Tree/fa. Nubia = cloud/felhő.
Más forrásból: Hebrew has been incorporated into this particular dialect of Papiamentu. Toward the end of the dictionary there is a short list of words comparing papiamentu sefardí with papiamentu komun, some
examples of which are afora (pap. sefardi) —afó (pap. komun.), bizjitá—bishitá, di repente—di ripiente, festehá—selebrá, mata di roza—mata di rosa, Saba—djasabra [dia sábado], tur kiko—tur loke.
Wanderers - kunhalom építő barbárok?
Hitler rokonsága, az E1b y haplogroup kimagasló arányban van a berbereknél.
The prehistoric people of Missouri not only had developed a great urban civilization based upon an agrarian economy but also constructed giant edifices of earth and stone. This same race was also capable of constructing the ingenious system of interlocking canals. With amazing skill, the engineers developed an internal system of navigation, linking the lakes and rivers with the various metropolitan centers of the region, and it was by means of these interconnecting waterways that the cities received the needed produce. The Mississippi River served as the principal transportation artery. Dr. G.C. Swallow, in referring to one of these canals, said, "One of them, that I examined, measured 53 feet wide and was 14 feet deep."
Evidence indicates the Mound-building Berbers or Tallegwi spread their Berber-derived language throughout Wisconsin -- and in the Mississippi and Ohio Valleys as far south as Memphis, Tennessee. By comparing basic Berber vocabulary with vocabulary from dozens of American Indian language families, R. Ben Madison tried to see if one or more such families had any significant resemblance to Berber.
Öntözött az egész ókori világ. Dél-Amerika is ezt tette... Vagy a pueblok népe.. Tiahuanaco built ingenuous raised fields surrounded by twisting water channels, known as suka kollus. Not only providing water for crops, the irrigation channels also absorbed heat from the sun during the day and released it at night to protect crops from frost and freezing – a necessary innovation when your average daily temperature is less than 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius).
Kína is öntözött. Illetve minden száraz terület népe, pl a Turáni-alföldé is. The irrigation works in ancient Sri Lanka, the earliest dating from about 300 BC, in the reign of King Pandukabhaya. Parakrama Samudraya consists three tanks and they are Thopa Wewa, Dumbutulu Wewa, and Erabadu Wewa.
Fantasztikus történet
Akadnak, akik NW-Africa (Mauritania) népét tekintik Amerika kunhalom építőinek. (Mound builders). Utalnak az mtDNA-ra is, hogy Amerika bennszülött lakossága az "A, B, C, D" mtDNA csoportokba sorolható, de egy el nem hanyagolható mennyiség a Nagy Tavak felé hordozza a misztikus "X" mtDNA-t.
Berber project
Serious work on "ancient Talossan history" didn't begin until the spring of 1985, by which time my Celts had transmogrified themselves into North African Berbers. The first (1985) edition of my History of the Kingdom of Talossa spent 45 pages outlining how Berbers had migrated from North Africa to
Western Europe, and that they had some hand in building Indian mounds in Milwaukee.
Az X mtDNA
Az antok vize: The widespread presence of the X type from Canada and Washington State, to Arizona, to the Plains, to the Great Lakes area, could indicate a wide initial dispersal. The X type in ancient America appears to be linked to the Iroquois tribe. This tribe, of course, was, according to Cayce, partly the remnant of Atlantean survivors from its final destruction about 10,000 B.C.
Egy fokkal hitelesebben: Archaeologists and geneticists are certain that the presence of "X" in America is not the result of historic intermarriages. It is of ancient origin. In addition, the 'X’ type has now been found in the ancient remains of the Basque. Among Native American tribes, the X haplogroup has been found in small numbers in the Yakima, Sioux, and Navaho tribes. It has been found to a larger degree in the Ojibway, Oneota, and Nuu-Chah-Nulth tribes.
Egyetemi: In contrast with the distribution of haplogroups A to D, haplogroup X is found nearly exclusively in North American populations. Interestingly, it occurs at its highest frequencies among Algonkian-speaking groups such as the Ojibwa, with all four of the Amerindian sublineages being present with this population. This mtDNA lineage has also been detected in two pre-Columbian North American populations and may be present in a few ancient Brazilian samples.
Töretlenül: A "fehér" gén: take a look - druze 28%, some hutterites X2c1 30%, american indians-up to 25%, these jungle amazon indians 15%, caucasus 8%, and the orkneys 8%..
Berber: mtDNA tartalmaz kiseb mértékben X1 és X2 típust is, ami néhol akár 35%-ot is elérhet. Mondjuk, ez a cigányoknál is előfordul, meg a baranyai vlax (oláh) népnél.
Builder Mound csoport
These skulls are neither dolichocephalic nor brachycephalic ; therefore we can neither look to the ancestry of the Red Men, nor to the Asiatic type, for the progenitors of the Mound-builders, who may justly be considered the autochthones of America. ..the length of any skull being represented by 100, the "cephalic index" is the proportion of this 100 covered by the breadth. These mounds are divided into three classes, according to their use.
Aukan nyelv The Aukan language is spoken by a group of people of African descent who were brought to Suriname against their will about 300 years ago and forced to work as slaves on plantations.
Aukan-English vocabulary: "afraid of, be vt. feele". Amerindian n. Ingii. ancestor n. afo. bathe vt. wasi. sama n. people; person. bird n. foo. kapata vi. scratch or dig the dirt by an animal. chop down trees vt. faa. makandaa adv. together. kelen vi. climb. diingi vt. drink. akwenda n. small person. tan vi. live; dwell. apaiti adj. holy. wolufu n. cloud. yooka n. spirit of the dead; ghost. motyo vi. be a whore.
Saamaka: Saramaccan (autonym: Saamáka) is a creole language spoken by about 24,000 ethnic African people near the Saramacca and upper Suriname Rivers in Suriname (formerly also known as Dutch Guyana), and 2,000 in French Guiana.
Saramaka dict.
ahún= grass. hánza= wing. hulu= to frequent person or place. hútu= bird type (great jacamar). peégu= nail. baasá= embrace; to embrace. baákúwáta= well. bajá= dance; to dance. bése= large frog/nagy BEKA. (Békás hékás?)
Pacific
Óceánia: Baga
The Oceanic Languages, Their Grammatical Structure, Vocabulary, and Origin
Today, the Baga people, 60,000 in total, occupy the northern coast of Guinea ...
"Neela" is the Hindi word for the colour Blue. The word "Bagh" also means a garden in Hindi. The word "Valley" in Hindi is called a "Ghaati".
Polinéz - Pikiram nyelve
Hamu/Ash: ti ahe tokoria (fire dirt)
Balta/Axe: tarai
Mell/Breast: tinae
Égni/Burn: vere
|
Táncoló hely/Dancing-place: ti tuva
Rossz szellem/Demon: ti aitu
Hal/Fish: kumi ika
Sírhely/Grave: ti tab
|
Ház/House: ti hare
Hold, hónap/Moon, month: ti maram
Név/Name: ingo
Orr/Nose: ti ushu
|
Húz/Pull: hutia
Tenger/Sea: tai
Kis/Small: turi
Nap/Sun: ti ra
|
Oceania
*rimay ‘to speak’
yawar [yawaˇ] ‘blood’
colour – kulli = purple; waita = flower in Quechua
Solanum kulliwaita
Érdekességként: A tagalog (és hiligaynon) nyelvekben a "girl/lány=dalaga", ami hasonlít a mongol "dologhan=7" szóra. A dolgan népnél a "7=hette", viszont a ngaan-asan nép biztosra ment. Náluk a "7=sitidhete".
Fülöp szk - Hiligaynon
butá = blind
balatáan = (anatomy) uterus, womb
balátas = galaxy
balátong = vegetables
balasón = sandy
árpa = harp, lyre. Italian: arpa f (plural arpe) harp (musical instrument) claw
halaran = altar
musika = music
Simbari nyelv New-Guinea: eye = simta. moon = lampaaka. ..és még pár szem. Érdekességként megjegyzem, hogy a SIAR nyelvben "yah=fire", ami szinte szemantikai ellentéte a jég szavunknak, valamint a "kés =to sit" > sék.
Fiji:
magaj n. brain, intellect [from Urdu maghz]
mahal n. palace [from Urdu]
makrra n. spider [from Hindi]
kabar n. grave [from Urdu qabr], kabrastaan - cemetery, graveyard
Hawaiian: stallion=Lio laho, lio ke'a. Keep out=kapu. Hawk=Io. (Mary Kawena Pukui)
Mu-lo idő
Ázsiai rokon
Some famous linguists like Edwin Pulleyblank believe that there are certain relationship between Sino-Tibetan, Tibeto-Burman and the Athabascan group of Native American languages, including Navaho, Apache, Eskimo ethnic tribes.
In a study conducted by Mexican archeologist Neil Steede of the National Institute of Anthropology and History, he discovered that 3,671 bricks had inscriptions. Of these bricks, 2,129 had Mayan inscriptions on them. But 499 of the bricks were found to have completely out of place inscriptions. 13.6% of the bricks were found to have Old World inscriptions on them. These inscriptions include writing in Arabic, Phoenician, Libyan, Egyptian, Ogam, Tifinag, Chinese, Burmese, and Paliburmese.
Hopi
The Tibetan word for "sun" is the Hopi word for "moon" and the Hopi word for "sun" is the Tibetan word for "moon". Hopi taawa for ‘sun’ does look a whole lot like Tibetan daawa for ‘moon.’
Turk rokon
Turk America
Phoenicia. He was considered as the leading authority on these hardy mariners. But even he was off base. He said that the Phoenicians had no definite homeland but occupied trading ports all over the Middle East. In the Western hemisphere, they were called Puni but did not usually answer to that name. Furthermore, he said they were a Mediterranean people. Yet, in studying Hindu history, I discovered that they also existed in Central Asia and India. But there, they were called Pani. Not even in India did they call themselves Pani.
Világnyelv
Tikal: "Tik" is one of the earliest root-words originating from the Proto-language, meaning "single, unique" which evolved to mean "finger" and "hand" (4). In all Altaic languages (Turkish, Uighur, Chuvash, Chagatai) "tek" means single. In the Eskimo-Aleut languages "tik" means the index finger. In Chinese "tiek" means one. In Atapascan languages "tek" and "tikhi" mean again one. In Amerind languages the Mixe say "tuk" and the Quiche Maya say "tik" for one. Therefore, Tikal means "The single one", or "Be unique" since the suffix –al exists in Turkish in the form of –il. Thus Tikal is the equivalent of "tekil" and means "singular" or "one of a kind". ..még turk.
Fantázia?
Csicsáky a maja nevet megmagyarítja, és immár magyáknak nevezi Mu őslakóinak legvitézebb és uralkodó törzsét. (Vagy csak a mangyan népre gondolt a filippinoknál?) Churchward claimed that the ancient Egyptian sun-god Ra originated with the Mu; he claimed that "Rah" was the word which the Naacals used for "sun" as well as for their god and rulers. Mu története angol nyelven és magyarul valami. És egy mesevideo.
Ra-jah: Sokan rokonítják a Rg, Ri, Regis, Rigan, Rex szavakkal. Vajh Jahmes ezzel egyetértene Ra isten földjén? ..és Rangi? Rangi is the god of the sky. Rangi (heavens), Ranginui (great heavens), Rangiroa (expansive heavens). Rajah: szláv nyelvekben égi, mennyei. Na jah. A Nappal ellentétben, a Hold nem tűnik óceániai eredetűnek. Kurd nyelven a "Nap=roj". Szinte "roy". (A madár panjabi nyelven panchhi.) Tibetben a gonosz szellem: Rahyangs (pronounced rodjung, rodzsung, rahdjang). Vajh a rossz szellem kapcsolatba hozható a "ro=kapu" szóval? Persian "rooh=ghost".
A Pacific nyugati peremén - halmozottan hátrányos
Tokár halmok a Fülöp szigeteken. Kunhalmok?
Bohol is an island in the Philippines in the Visayas power plants, with an area of 117.3 km 2 4 Its uniqueness is the site of Chocolate Hills, consisting of approximately 1776 hills, cone-shaped, of about the same size, and spread over 50 square kilometers The cones are 30 to 50m high and up to 120m wide. Más honlapról mutatva, valamint Ady verse, az Ős kayan..:-) Eskayan is a language isolate spoken on the Philippine island of Bohol.
The Chocolate Hills are conical karst hills similar to those seen in the limestone regions of Slovenia, Croatia, northern Puerto Rico, and Pinar del Rio Province, Cuba. Fűvel borított mészkődombok. Precízebben erodálódott, víz fölé került koralltelepek állítólag. Helyzetük 100-500 m a tengerszint felett. Magasságuk 30-120 m.
Geológia.
Butább szelek műve:.
Okosabbé.
Mészkő erózió, Kína.
Óceánia V.rész
Amerika 1.rész
Amerika 12.rész
Pesti István 2014 november
Nyitóoldal

 A szibériai nyelvekhez hasonlóan a kettős szám jele a "-k", a többes számé pedig a "-t". Lándzsa = pana-m. 2 lándzsa = pana-k. Több lándzsa pedig pana-t. A filippino lándzsa "sibat". Náluk a pana az "íj és a nyíl".
A szibériai nyelvekhez hasonlóan a kettős szám jele a "-k", a többes számé pedig a "-t". Lándzsa = pana-m. 2 lándzsa = pana-k. Több lándzsa pedig pana-t. A filippino lándzsa "sibat". Náluk a pana az "íj és a nyíl".  Pre-Columbian art
Pre-Columbian art Régi címerünkben jobban hasonlít az Ücs tepét az apostoli kereszttel összekötő kép a liliomra, mint egy koronára. Mai címerábrázolásunkban direkt hangsúlyozzák a korona képet. A margitszigeti és az egyik koreai korona is liliom-szerű formákkal van bekerítve. Vagy csak stilizált turul madár?
Régi címerünkben jobban hasonlít az Ücs tepét az apostoli kereszttel összekötő kép a liliomra, mint egy koronára. Mai címerábrázolásunkban direkt hangsúlyozzák a korona képet. A margitszigeti és az egyik koreai korona is liliom-szerű formákkal van bekerítve. Vagy csak stilizált turul madár?