

 Andok
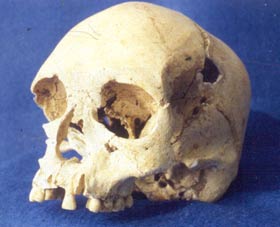
Andok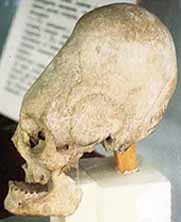 Koponyatorzítás Arica területén:
Koponyatorzítás Arica területén: |
Ennead: A korai vallás öt területileg elkülönülő csoportra osztható: |
 AYMARA
AYMARA Turistaút Chilében.
Turistaút Chilében. 
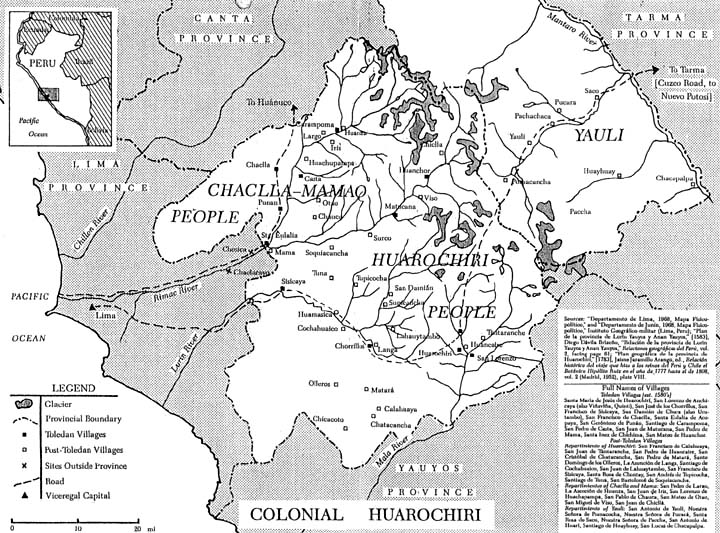 PERUI KAPCSOLAT
PERUI KAPCSOLAT |
APA szavunk pár nyelven: |
AZ ÚR SZAVUNK | ANYA
szavunk |
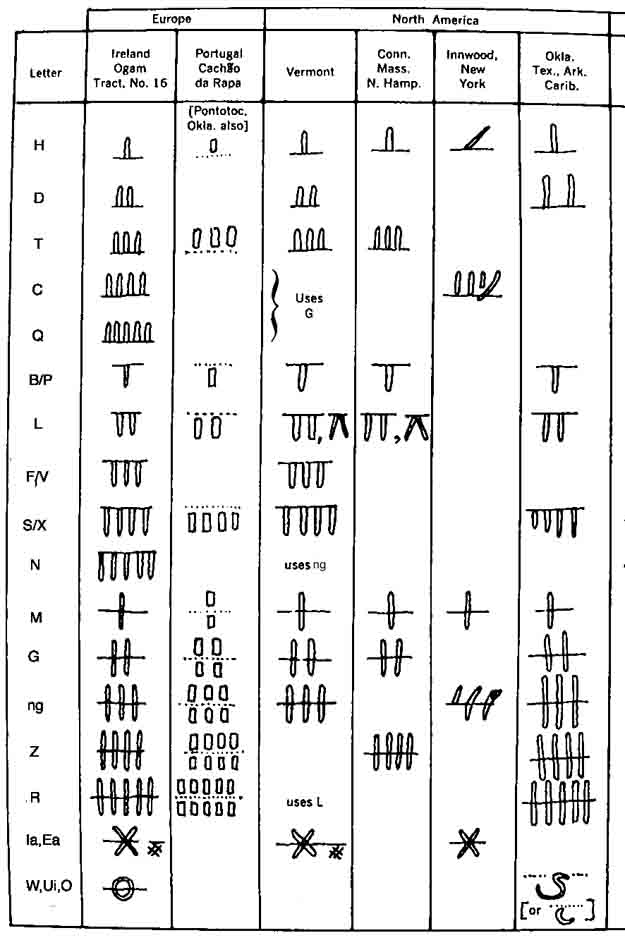 OGHAM - 2 ezer évvel a sumer írás után
OGHAM - 2 ezer évvel a sumer írás után 
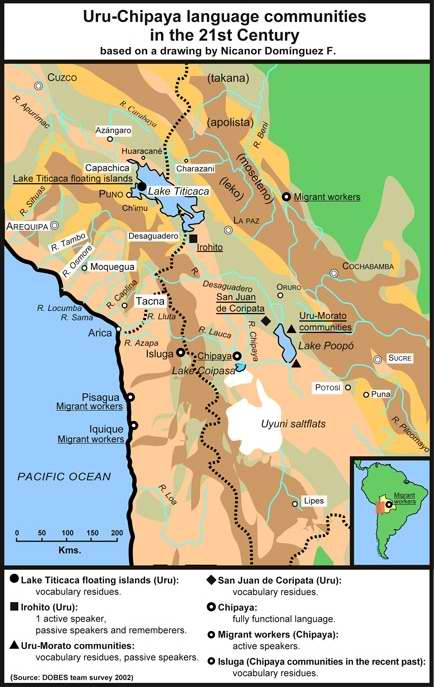 Inkák a spanyolok
előtt
Inkák a spanyolok
előtt  Otavalo
Otavalo 
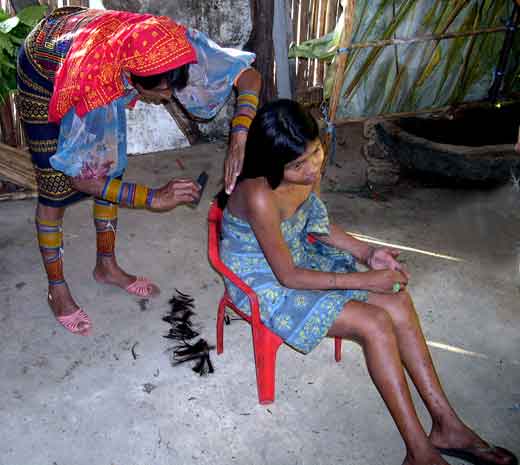 Ünnep Amerikában:
Ünnep Amerikában: 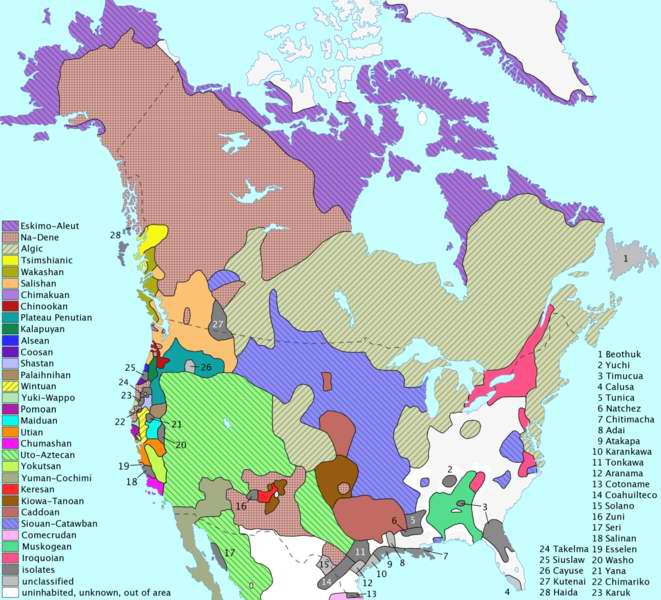 Tanana are an American Indian group located in Alaska. The name Tanana is a corruption of the Tanana Athapaskan term Ten Dona' which refers to the Tanana River valley. Among Tanana Athapaskans the term used for the Tanana River proper is Tth'eetoo', meaning straight water. The names cited in historical accounts reflect the term applied by neighboring Gwich'in ("Kutchin") Athapaskan groups of the Yukon River valley. The Tanana Athapaskans do not refer to themselves by this larger grouping, but
rather by the individual band name, such as Mentekhut'ana
(people who inhabit the Minto Lakes).
Tanana are an American Indian group located in Alaska. The name Tanana is a corruption of the Tanana Athapaskan term Ten Dona' which refers to the Tanana River valley. Among Tanana Athapaskans the term used for the Tanana River proper is Tth'eetoo', meaning straight water. The names cited in historical accounts reflect the term applied by neighboring Gwich'in ("Kutchin") Athapaskan groups of the Yukon River valley. The Tanana Athapaskans do not refer to themselves by this larger grouping, but
rather by the individual band name, such as Mentekhut'ana
(people who inhabit the Minto Lakes). Na Dene
Na Dene
 |

| |
Phoenician style hut found in Tibet, Similar to Tupas on Easter Island and Chulpas in Peru
Név "Hajnal Latin-American name In Latin-American, the name Hajnal means- dawn."
Inkák EurópábanPesti István
Vissza az Amerika 1. lapra.