Afrika 4.
Ant
Tó, amely folyik
(Garda tó, Észak_itália: Egy folyó kövér szakasza.)
The author here recontructs a hypothetical ancestor verb *garda "to sink" and claims that its root *gar is a noun cognate with garam(?) "river" and geor(?) "rivulet."
In response, it may be said that the river flows ripping the earth, while the ship sails forward ripping the water, and often sinks down to the bottom so doing as well, hence perhaps no use of such reconstruction!
Ha a GARAM az "folyó", akkor a Garam-ant az "folyami ant" ?
pismire - Mauritania
late 14c., from pyss "urine" (in reference to the acrid smell of an anthill) + mire "an ant," probably from O.N. maurr "ant," perhaps distantly connected with Gk. myrmex, L. formica "ant." Cf. pissant, also early Du. mierseycke (from seycke "urine"), Finn. kusiainen (from kusi "urine").
*moru¸i- `ant'
Etymology: For the formation cf. skčlhx, sf»x a.o. (Schwyzer 497, Chantraine Form. 380 f.); a velar suffix, prob. without genetic connection with mÚrmhx, is also seen in Lat. form–ca `ant' and Skt. valm–ka- m. n. `ant-hill'. -- The basis is seen in different forms in many IE languages, mostly with anlaut. m and in-(aus)laut. -u¸-, also with inlaut. -r-: IE *moru¸-– ˘in Av. maoiri-, Celt., e.g. OIr. moirb, Slav., e.g. ORuss. morovij; IE *mour-, *meur- in Germ., e.g. OWNo. maurr -n. (PGm. *maura-), OSwed. myra f. (PGm. *meuriˇn-). Besides with anlaut. u¸- and inlaut. -m- : Skt. vamra´- m. (cf. valm–ka above), thus bŇrmax, bÚrmax with b- for F-; in Órmikaj a F- may have been lost.
Khinalug root: ant
North Caucasian etymology: 2191
Meaning: earth, ground
Khinalug form: ant
Comments: The root serves as a base for ant:?r-q˙i 'to lie' (= 'to be on the ground').
Ant
..to wit: wit(ant)- "year", gim(ant)- "winter", zena(nt)- "autumn"...
...garra "claw"...
Érdekességnek:
Kond
GOND is a name given to tribes by non-tribals, which etymologically means a forest dweller. {erdőlakó. P.I.}....
In Telugu, Kond means a mountain and hence Kond/Khond or Gond means forest dwellers....
The Gonds are subdivided into sub-groups or sub-tribes viz. the Raj-Gond, and the Madia/Maria-Gond. Among the Maria/Madia-Gond there are the Bada-Madia who are ...
Só = Salt = Garam (malay)
Tuareg
The Tuareg or Blue Men of the Sahara have captivated popular imagination in the West for centuries. ...
They were renowned for their fierce struggles against other desert nomads like the Chaamba Bedouins in Central Algeria ..
The Imazighen descend from Capsian Man, a Homo Sapiens hunter-gatherer who evolved in Capsa (Gafsa, Tunisia) on the shores of lake Chott El-Jerid around 10,000 BC.
Írásuk a 3.századig használatos TIFINAG abc. "tifin=mienk" és "nag=fejlesztés". Más magyarázat szerint "taffineqq=föníciai betü".
Szülőföld - Afrika
Afri was the name of several peoples who dwelt in North Africa near Carthage. Their name is usually connected with Phoenician afar, "dust", but a 1981 theory has asserted that it stems from a Berber word ifri or Ifran meaning "cave", in reference to cave dwellers. Africa or Ifri or Afer is name of Banu Ifran from Algeria and Tripolitania (Berber Tribe of Yafran).
the Egyptian af-rui-ka, "to turn toward the opening of the Ka."
Kis vita
Térkép
Másik map
Ifriqiya - érdekességnek
Mysterious Queen of Algerian Israelite and Amazigh peoples. When the Islamized Arabs invaded the Maghreb, al-Kahina first raised the cry "Africa for Africans". (At that time, the late 7th century, only the Mediterranean littoral was known as Africa (Ifriqiya)
the White Jews whose skins are white as snow who have attached themselves with the Tuareg, but who are gentically different. They say the original Jews from Cyrene were White and some present Jews in southern Morocco and areas south are Black because Black slaves joined up with the Jews.
Hun kor
The letter of Phonen, found in 1976 in Qasr Ibrim (in Lower Nubia), is written on papyrus in poor Greek which makes it rather difficult to interpret (Eide et al.1998). It was written by Phonen, who identifies himself as King (ß???????) of the Blemmyes, and is addressed to Abourni, King of the Noubades, and his sons.
Egyiptom királya
Black Athena
Heftalita nyelv?
???????? ???????? ????š??? - De honnét jöttek a szlávok?
Basileus
Érdekességnek: - A fárao neve (angol nyelven)
A skótoknak is tetszett a cím. Magyar változat.
Az írás
For instance (basileus, king) is written as pa-si-le-u-se.
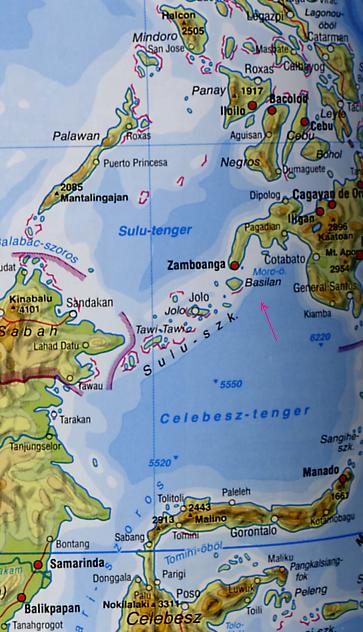
Ba·si·lan (bä se'län),
largest island of the Sulu Archipelago, the Philippines, southwest of Mindanao: 495 sq mi (1,282 sq km)
Eritreánban (Eritrea térkép) 5 nyelvet beszélnek, ezek egyike a saho. A SAHO szó
Japánban sem ismeretlen..
Milyen véletlen, hogy Nara közelében bukkant fel a saho szó Japánban!
"There are 9 ethnic groups; Tigrinya, Tigre, Kunama, Saho, Afar, Belen, Rashida, Hidarb and Nara "
A member of the nomadic Muslim tribe, the Saho, she lives in Sefira, a town about 120 kilometres south of the capital, Asmara, near the dramatic heights
of the 2,400-metre high Qohaito plateau.
Érdekességnek a "write horse" népe:
" that the Gar at Orm's Head means the Snake's Head"
...még házalunk..
Harari Vocabulary
hangür (harari)= torok; Wolane angaro s Zway angäro Chusitic kölcsönszó?gäza = move from the house (HÁZ)läm = cow (tehén)buda = a man who has the power of casting the evil eye = mágus
Érdekességnek:Amazon - egy madárféle.
Viszont: Proto-Germanic: *angara-z, *angira-z Meaning: worm (féreg)
Ami még érdekesebb:Old Norse: eng f. `Wiese'; engi n.; -ang-r m. (in ON: Harđangr, Stafangr) `Bucht'Swedish: äng `Wiese'; Harm?ngerOld English: { ing `akkerland' }Middle English: eng, ing `Wiese'English: dial. ing Wiese'
Baron-Tala
Klaproth states that the Mongols applied to Tibet the name of Baron-tala, signifying the "Right Side," i.e. the south-west or south quarter, whilst Mongolia was called Dzoehn (or Dzegun) Tala, i.e. the "Left," or north-east side. It is possible that Chigin-talas might represent Dzegun Tala in some like application. The etymology of Dzungaria, a name which in modern times covers the territory of which we are speaking, is similar.
Arigar - Angkor
Madarak jönnek..
Buret is the archaeological memorial, extremely similar to Malta, it is placed on the right bank of the Angara. It was analyzed by the known Siberian archaeologist A. Okladnikov. Radiocarbon date of the bones, made in 1980, gave the date of 21190 years ago.
A csornai diadém
Kalasha as an Indo-Aryan language, closely related to Khowar: "Probably the two languages belong to the first wave of Indo-Aryan immigrants from the south" (Morgenstierne 1932: 51).
pac'hiyak = 'bird'
angar = fire
ek = egy
Kanurak
Makarisztán
v
Mangbetu culture has affected especially the Medje, BaLika, WaBudu, and a part of the BaNdaka.
MaBudu
Budu [buu"> 180,000 (1991 SIL). Orientale Province, Wamba Territory. 8 collectivités. Alternate names: Bodo, Ebudu, Kibudu. Dialects: Ineta (Timoniko), Wadimbisa (Isombi), Makoda, West Bafwangada (Bafanio), East Bafwangada, Bafwakoyi, Malamba, Mahaa.
Bushoong [buf"> 155,000 (2000). Kasai Occidental Province, Mweka and north Ilebo territories. Alternate names: Bamongo, Bushong, Bushongo, Busoong, Ganga, Kuba, Mbale, Mongo, Shongo.
Hungana {hum} 400. Bandundu Province, Bulungu Territory. Alternate names: Huana, Hungaan, Hunganna, Kihungana.
Kari {kbj} 1,000. Northwest Orientale Province scattered, north of Uele River.
Lika {lik} 60,000 (1989 SIL). 57,000 in Wamba District, 3,000 in Rungu District. Orientale Province, Upper-Uele District Ma {msj} 4,700 (Voegelin and Voegelin 1977). Orientale Province, north of Niangara, near Kapili River. Alternate names: Amadi, Madi, Madyo.
Megyer törzs
Meegye is regarded by most outsiders as a dialect of Mangbetu. By the same outsiders’ view, the Mangbetu language’s other dialects are Mangbetu proper, Makere, Malele, Mapopoi, and Mabelu.
Megye
Képekben
La langue des Makere, des Medje et des Mangbetu (Library Binding) Currently unavailable.
Fantasztikus fejek
linkek
Hunok, lombardok és mások..
Cerulli used the term "Galla" to designate the people that now call themselves "Oromo."
Borana or Eastern Galla dialects. (Bor-ana is derived form the root bor, "east/kelet.")
Gari-funa
Lidangien lamuri bian barana. Labugien larüna funati luma golu. Barumuga lau lirufungu ketsali ... Ubugua lun dari me lan lahamachun. Inu lan luei kondoru luma garun ...
Blench és Koelle munkáiból még: (szintén kanuri nyelv)
söbduwa söbdu < Arabic ‘Saturday’ (sabat) 7, szombat
paltu ?al?u ‘to change’
bakta? bakta (Standard) ‘shroud’
da?ka damga ‘hawk’
köndé, k?` nda?i, k?` nda? i ‘basket’ (kosár, kondér?)
'Igaboo', contemptuous term for Isoko. Clarke 'Egarra' (Yoruba), 'Eggara'/'Igarra' (Igara); Koelle IV 8a. 'Egura'.
Kanuri - angol szótár
Ámbörika = Amerika
avör = köpködő kobra
ballá = határkő
börbör = por
böröt = emphasizes action of two people falling down simultaneously.
börnyi = székhely
bül = fehér
cár = keménység
Nigéria
Blench és Koelle
(angol, magyar, niger)
dog = kutya = ebu:s?, i-mabç, a-
son = fia = ow?, vő
father = apa, atya = ada-am, ada
man = férfi = o-sag, a-; úsú, ásák
house = ház, kunyhó = undju, a-; ku-ncu, a-
nine = kilenc = tola; tora
maize = kukorica, nem búza = vúza; u:guza,
branch = ág, csoport = o-nâp, e-
eye = szem = ku-su, a-; u-su, a-
farm = tanya? = a-lúm; e-la:m, E-
village = falu = u-tep,a-; u:-teb;
slave = szolga = -; o:-gala
Cameroon pár nyelve:
Nyelv : alternatív elnevezés, dialektus
Duala : Ewodi, Ouri, Uli, Wuri, Wouri
Dugun: Panon, Pa'non, Pani, Saa, Pape
Dzodinka: Arderi
Fali: Peske, Bori, Kangu
Fe'fe': Bana, Balafi
Fulfulde, Adamawa: Fulbe, Palata, Sanyo, Garoua
Fulfulde: Kano-Katsina, Bororro, Ako
Gavar: Gawar, Gouwar, Gauar, Ma-Gavar.
Gbaya: Baya, Kalla
Hdi: Hide, Turu-Hide, Tur
Kanuri: "Beriberi", Kanouri, Bornouan. Movar, Dagara, Kabari , Maiduguri.
Kare: Kali
Kenyang: Banyang, Manyang. Bakoni , Manyeman, Kicwe, Kitwii,
Kom: Itangikom, Kong
Kwakum: Abakum, Baki
Mada
Makaa: Mekaa
Malimba: Lemba
Maslam: (Makari Subdivision, in Maltam )
Mofu: Douvangar
Mofu-Gudur: Mokong
Mpade: Makari, Makary, Mandage, Mandagué
Mser: Kuseri, Kousseri, Mandage. Kalo
Mundani: Banti, Bangang
Mungaka: Bali, Ti (Bati)
Musey: Bananna Ho, Ho
Ngambay: Sara, Gamba, Gambaye
Ngie: Ungie, Mingi
Nsari: Akweto, Pesaa, Sali
Tikar: Tikali, Tige, Kong
Tsuvan: Teleki
Vengo: Babungo, Vengoo, Vengi,
Wandala: Mandara, Mura. Kirdi-Mora
Wuzlam: (Mayo-Sava Division)
Nyelvi térkép:
Pár szó nigéria nyelveihez
Hivatalos nyelvek: Edo, Efik, Adamawa Fulfulde, Hausa, Idoma, Igbo, Yerwa Kanuri, Yoruba, English.
az Ádáméva "Fulfulde" akár "felfölde" is lehetne. Az "Edo" nekem Japán/Nihon területéről ismert, de még lehetne belemagyarázni a többibe is valamit.
Nem hivatalos nyelvek Nigeriában: cca 500 nyelv !
Ebből a fülemnek ismerősen cseng 62:
WAPAN (JUKUN),
WANNU (RIVER JUKUN),
WANDALA (MANDARA, MALGWA, KIRAWA),
VEMGO-MABAS (VIZIK),
VAGHAT-YA-BIJIM-LEGERI (TIYA, BOI)
TULA (KUTULE),
TANGALE (TURE),
TALA (Kuka and Talan Kasa villages),
SUKUR (SAKUL),
SIRI (SIRAWA),
SHOO-MINDA-NYE (A Sumida folyóra emlékeztet),
SHANGA (SHONGAWA) (Folyó szó Indokínában + Japánban)
SAMBA DAKA (CHAMBA DAKA) (A Brahmaputra vidékét idézi)
RON (NAFUNFIA)
PSIKYE (WULA)
MUMUYE (LANKAVIRI, BAJAMA, KASAA, SAAWA,SHAARI)
MAK (PANYAM, PANYA)
MÁGHDI (TALA)
MADA (MADDA, YIDDA)
MAAKA (MAHA, MAKA, MAGA, MAGHA)
LURI
LUFU
LOO (LO, LOH, SHUNHU)
LONGUDA (NUNGURABA, NUNGURA, LANGUDA, LONGURA)
LAMJA-DENGSA-TOLA
KUSHI
KPAN (ABAKAN, APA)
KOFA ( KOTA)
KIR-BALAR
KAREKARE (BIRKAI)
KANURI (KABARI, KUVURI)
KAKANDA (BUDON KAKANDA) Buda környékén.
KAAN (LIBBO, KAN)
ISEKIRI (SHEKIRI, CHEKIRI, WARRI) (Yoruboid, Edekiri.)
IKWERE (APANI, TOLU, ISIOKPO)
IDUN (UNGU)
HUNGWORO (UNGWE)
HUN-SAARE (HUN, ET-HUN, HUNE)
HUBA (CHOBBA)
HOROM
HOLMA (BALI HOLMA)
GALAMBU (GALAMBI)
FYAM (PAIEM)
FUNGWA (URA, ULA)
FULFULDE (BORORO, AKO, SOKOTO)
FALI (URA MADZARIN)
ETULO (ETURO, UTUR, TURUMAWA)
ESAN (ISHAN, ISA, ESA)
EPIE (ATISA /ATISSA/) (delta)
DUNGU (DUNJAWA)
DUGURI (GAR DUGURI, BADARA DUGURI)
CIBAK (CHIBUK)
CHE (KUCHE, INCHAZI)
BUDUMA (BUDUMA, KURI)
BOGA (BOKA)
BEROM (BIROM, ABORO, KURU-VWANG)
BAUCHI (BAUSHI, KUSHI,MADAKA)
BATA (BIRSA, DUNU)
BADA (KANNA, JAR, JARAWAN KOGI, GARAKA)
BAAN (KA-BAN, KESARI)
ASHE (KORON ACHE, KORON ALA, KORO MAKAMA)
AFADE (MOGARI)
Nok, Nigéria
Nok was a West African civilization that flourished from about 700 B.C. Until at least A.D. 200.
Térkép - nok terület és Sokoto.
Hízókúra
Mindenesetre csak én neveztem hízlalásnak a folyamatot, a valóságban a helyiek ezt Nkuho néven illetik, és a nővé válás folyamatának tartják. És ha valaki a google-n rákeres calabari efik nőkre, tisztán látható, hogy egyáltalán nem formátlanul kövér emberekről, hanem telt lányokról beszélünk, akikkel bármely más országban találkozhatunk.
Vár állott...
Nok ember - Ilyenek voltak, vagy csak művészi túlkapás?
Torzult koponya, mandulavágású szem.
A világ 7. legnépesebb országa a jelenleg 148 milliós Nigéria, ahol a statisztikusok szerint 2050-re várhatóan 282 millióan lesznek. De mit esznek majd?
Ancient
The primitive iron-smelting furnaces at Taruga dating from the fourth century B.C. provide the oldest evidence of metalworking in West Africa, while excavations for the Kainji Dam revealed the presence of ironworking there by the second century B.C. The transition from Neolithic times to the Iron Age apparently was achieved without intermediate bronze production.
The presence of R1* Y chromosomes in Cameroon is considered as evidence of a back migration from Eurasia into Sub-Saharan Africa.
All mtDNAs were assigned to five haplogroups: three sub-Saharan (L1, L2, and L3), one northern African (U6), and one European (U5).
Modern térkép
Rosszabb de jobb
Art - etruszk korinthoszi? sisakban
Marghi
Margi, also known as Marghi and Marghi Central, is a Chadic language spoken in Nigeria. It is perhaps the best described of the Biu-Mandara branch of that family. Marghi South and Patai are sometimes considered to be dialects of or closely related to Margi, sometimes groups with other Bura-Margi languages
Greek
that category the Bura "sha", the Babur, the Chibok and Marghi, all of whom speak the Bura language, which phonologically is similar to Bantu and also, interestingly, has some words identical with some Greek words. Wide linguistic influence might not be ruled out, for Bura language is spoken over a large area, stretching to French Cameroon in the East and almost to the Benue in the West.
That’s what marg is: a new way
whereas purush is consciousness
Therefore the love of Pururava for Urvashi is his attempt to find nature (prakriti) and his own nature (svabhav) within himself.
Nigeria nyelvei
Huba, Chobba, Hunne, Hwana, Hona
“Marghidun” or “Marghidunum” in Arthurian times, from “marghi” boundary, and “dun” or “dunum”. Latinized “hill fort”, in other words
The Kapsiki of Cameroon live on the central plateau about 900m high south of Mokolo, connecting the Northern Mandaras and the Southern Mandaras
Sztárok a világban.
Kelet-Afrika
Zimbabwe
A zsidó papok földje
The ancient ruins known as Zimbabwe, where the soapstone carving of the bird was found, lie in the heart of the territory now occupied by the Mashona tribe, though it is not thought that they are the same people who founded the ancient civilization.
Zimbabwe
Mashona
Érdekességnek: Zimbabwe romjai térkép.
Kichagga
KI-Chagga, vagyis chagga nyelv. A chagga "nap" jelentésű... (mennyire hasonlít a csakra szóra!)
Színes ruhadarabjaik neve kangas. A főnök neve mangi
Ezek már magyarul sem tudnak!
"Maitü ni Ma Itü" ="Anyánk az igazságunk"
Nyelvészeknek: (hongera=thanks; kirao=nyilvessző tolla) "For eaxample kuri 'dog' is Cushitic and Mbugu" (quechua!)
Etiópia
Byss
Len szál
This word is to be distinguished from what might at first seem to relate to "depths," such as the "abyss." Byssinosis is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by the inhalation of fine particles of textile fibers. The Greek word for such a fine fiber is byssos or byssinos.
Thus, the word byss is attested in English to mean "fine linen."
A fine-textured linen of ancient times, used by the Egyptians for wrapping mummies.
Víz
In other words, a ‘waterless’ (Spiritless) black hole – an abysmal place. That ‘byss’ means ‘water’ can be seen in the Dutch word for drink, or ‘buzen’. Also, the letters ‘p’/’b’/’f’ could be and are, sometimes interchangeable i.e. our word ‘piss’ means ‘water’ and the word ‘fish’, too, is related to water.
English-Latin Online Dictionary: abyss
profundum, vorago
abyss the underworld: barathrum
Dictionary: a·byss (?-bis') pronunciation ... Abyss (from Greek ?ß????? = "bottomless", "the bottomless pit")
Len
A byssus és linum egymáshoz nagyon hasonlított, úgyhogy az írók majd az egyiket majd a másikat használják. A rómaiak inkább kedvelték a pamutkelméket mint a byssusból készült szöveteket.
Abyss= Delos?
Delos was called also Asteria, Pelasgia, Chlamydia, Lagia, Pyrpilis, Scythias, Mydia, and Ortygia.
The name Delos was commonly derived from ?????, “manifest,”
Latin szótárból:(Finály Henrik)
barathrum, i, kn. {= baraqron}
(többnyire költ.) örvény, mélység, feneketlen mélység, átv. ért. tréfásan a gyomorról: b. macelli = nagy bélü ember, kinek «pokol» a gyomra.
vorago, inis, nn. {voro}
1) torkolat, mélység, vizben örvény.
2) átv. ért. az elnyelés jelölésére: v. ventris, telhetetlen has; v. reipublicae, a polgárzat veszedelme (rosz polgárról); v. patrimonii, tékozló.
profundus, mn. kf. és ff. {profundus}
1) mély (felülről alá nézve a tárgyat, vesd ö. altus), mare; (költ.) az alvilágról és a hozzá tartozókról mélyen fekvő; (költ.) poeta profundo ore (folyóról vett kép) szódús. Innen fn. profundum, i, kn. mélység A) tenger mélysége, tenger. B) átv. ért. (újk.) p. miseriarum. C) (Pl.) tréfásan a gyomorról. D) t. profunda, orum, kn. az alvilág.
2) altus, magas; p. clum.
3) átv. ért. feneketlen, mérték felett való, tulságos s több efféle, cupiditas, libido. Innen fn. profundum, i, kn. feneketlen mélység;
||4) szellemileg mély, mélyre ható.
5) (újk.) ismeretlen.
6) átalában nagy kiterjedésü, széles, vastag, stb.: silva (magyarul is «mély»-nek mondjuk); grando, sűrü; ursi profundioribus villis, tömöttebb lombu szőrrel; fn. profundum, i, kn. magasság, mélység.
A latin szótárt figyelembe véve Abesszína inkább a "pokol"-t jelenti, mint egy, a szárazföldbe mélyen benyúló országot. Vagy "Hold-apót" (Abu-sin-ia).
TANA KERESÉS
We set up our tent while Gerard our guide who has come with us from Tana sets up his and the two girls we hired in Ranamofana start cooking lunch. Gerard is a Malagasy who lives in Tana. He belongs to the xxx tribe which is the highest ‘caste’ of the twelve Malagasy tribes....
Fly from Tana to Taolanaro (Fort Dauphin) in the deep south on MadAir (terrifying!). Taolanaro is a depressingly dirty, very poor town with lots of beggars, mostly kids.... (Ter. Madagaszkár déli részén)
A TANA típusú kerámiák (háromszög rajzolatú) megtalálhatóak Kelet-Afrikai partjai mentén, különösen AD 9-11. sz.-ból.
Szanszkritból maori: (ismétlés)
Kalenjin {Kalendzsin}
Kenya
Szalon-rasszizmus
...és a NANDI
"Traditional Kalenjin religion is based upon the belief in a supreme god, Asis or Cheptalel, who is represented in the form of the sun, although this is not God himself. Beneath Asis is Elat, who controls thunder and lightning. Spirits of the dead, oyik, are believed to intervene in the affairs of humans, and can be placated with sacrifices of meat and/or beer, called koros. Diviners, called orkoik, have magical powers and assist in appeals for rain or to end floods."
Highland-Nilotic nép
KOTA, avagy honnét jöttek a finnek? (gypsi leszármazás?)
"Mr arap Cherono is right in asking about Jewish-Talai nexus. If the Gypsies of Europe have their own Orkoiik,that is in order since the Gypsies have a common ancestry with the Kalenjin. Gypsy means out of Egypt. Egypt in turn is a Kalenjin name. Egypt is derived from the word Kagyptaiyaat ie the home of Kiptaiyaat - the Godhead of the Kalenjin. The English word royal is corrupted from the kalenjin word orkoi or Orkoiik. The Greeks used to refer to orkoiik as arkhont.The royal family of Great Britain should have also descended from orkoiik. Orkoiik is derived from two words, or or woor meaning big,chief and koot meaning house. Hence orkoiik should mean people of the big house ie respected people. I hope arap Cherono should shed more light on the Orkoiik of Gypsy(Proto-Kalenjin) who have been persecuted in Romania,Poland,East Germany and other parts of Europe."
A nagy tavaktól nyugatra. Aba vidéke:
Southern China was also occupied by mixed race we call 'Polynesians' WHO DID NOT ORIGINATE IN THE POLYNESIAN ISLANDS BUT IN SOUTHERN CHINA (Scientific American -- note; if you want to see the article, check http://www.sciam.com or google 'Scientific American,' )
Then one of the most important groups to add to the Chinese gene pool as well as language are the Kong and Ba-Kong people.
Kong are people of 'BUSHMAN' stock, who look like Chinese with Afros. The only difference is that some Chinese are very fairskinned and have straight hair. Kong, BaKong, Mangbetu, Mersi range from black skinned to yellowish-brown and all have kinky hair.
However, the Kong, BaKong, Southern BaNtu Mangbetu, Mersi and Hutus of Rwanda all have the Cde and M gene --- THE FOUNDING GENE FOR ALL 'MONGOLOID' PEOPLE INCLUDING Chinese, Japanese, Malays, Siberians and American Indians.
Hadza
"We analyzed genetic variation in 122 "unrelated" individuals from the vicinity of Lake Eyasi in north-central Tanzania, to recover aspects of population history and human evolution. Representatives of the four linguistic phyla of Africa were studied, including 50 Hadzabe (or Hadza) foragers.
References
habitation of Ituri Forest (in Ituri Forest (forest, Democratic Republic of the Congo): The Pygmies; in Ituri Forest (forest, Democratic Republic of the Congo): The village-living agriculturalists ) Other The following is a selection of items (artistic styles or groups, constructions, events, fictional characters, organizations, publications) associated with "Lese"
Képeskönyv
Medje Mangbetu statue
The Mangbetu came from modern day Sudan moving south coming into contact with the Azande.
Elongated skull
Térkép
Makarisztán
Mangbetu culture has affected especially the Medje, BaLika, WaBudu, and a part of the BaNdaka.
MaBudu
Budu {buu} 180,000 (1991 SIL). Orientale Province, Wamba Territory. 8 collectivités. Alternate names: Bodo, Ebudu, Kibudu. Dialects: Ineta (Timoniko), Wadimbisa (Isombi), Makoda, West Bafwangada (Bafanio), East Bafwangada, Bafwakoyi, Malamba, Mahaa.
Bushoong {buf} 155,000 (2000). Kasai Occidental Province, Mweka and north Ilebo territories. Alternate names: Bamongo, Bushong, Bushongo, Busoong, Ganga, Kuba, Mbale, Mongo, Shongo.
Hungana {hum} 400. Bandundu Province, Bulungu Territory. Alternate names: Huana, Hungaan, Hunganna, Kihungana.
Kari {kbj} 1,000. Northwest Orientale Province scattered, north of Uele River.
Lika {lik} 60,000 (1989 SIL). 57,000 in Wamba District, 3,000 in Rungu District. Orientale Province, Upper-Uele District Ma {msj} 4,700 (Voegelin and Voegelin 1977). Orientale Province, north of Niangara, near Kapili River. Alternate names: Amadi, Madi, Madyo.
Megyer törzs
Meegye is regarded by most outsiders as a dialect of Mangbetu. By the same outsiders’ view, the Mangbetu language’s other dialects are Mangbetu proper, Makere, Malele, Mapopoi, and Mabelu.
Megye
Képekben
La langue des Makere, des Medje et des Mangbetu (Library Binding) Currently unavailable.
Fantasztikus fejek
linkek
Hunok, lombardok és mások..
Cerulli used the term "Galla" to designate the people that now call themselves "Oromo."
Borana or Eastern Galla dialects. (Bor-ana is derived form the root bor, "east/kelet.")
Gari-funa
Lidangien lamuri bian barana. Labugien larüna funati luma golu. Barumuga lau lirufungu ketsali ... Ubugua lun dari me lan lahamachun. Inu lan luei kondoru luma garun ...
Zimbabwe
Nagy-Zimbabwe egy igen nagy területre kiterjedt bantu királyság fővárosa volt. A „Zimbabwe” szó kőházakat, bekerített udvart jelen. A város igen fontos kereskedelmi központként működött. A kutatások szerint kereskedelmi kapcsolatai egészen Kínáig elértek. A település a XV. századtól egészen a XVII. századig a birodalom fővárosa volt. A birodalom aranyat és elefántcsontot szállított az Indiai-óceán partvidékére, ahol az eladott áruk fejében textíliát és üveget vásárolt. Ezt a kialakult jól működő rendszert a portugálok megjelenése tette tönkre.
Tola
A vár legtitokzatosabb épülete a kúp alakú torony, melynek nincsenek ablakai, ajtaja, sem lépcsője. Egyenlőre nem tudják, hogy milyen célból építették
Említésre érdemes a még meglevő számos madárszobor, valamint a területen élő elveszett zsidó törzs, a bulba klán...
Afrika I.rész.
Afrika III.rész.
Pesti István 2010 március
Nyitóoldal
