India 7
A szubkontinens keresztje
Hitélet
Pater noster
..ki vogy az Manyukban.. (Tochar B. menye is Moon.)
I found that the most enlightened of these Zoroastrians look upon Ahura Mazda as comprising within himself the conflicting powers of good and evil, designated respectively as Spenta Mainyu, ‘Holy Spirit,‘ and Angra Mainyu, ‘Evil Spirit,’
Patri Ark-ák kora. (Az ar-k magában plural! S a patri nem éppen apa!)
Maori ősműveltség: PATARIKI: Maori form of Greek Patrikios, meaning "patrician, of noble descent". Hans Henrich Hock nyelvész "Principles of Historical Linguistics" munkájában a patrícius szó fejlődése a pre-OW patrikios > pre-OIr. qatrikias > OIr. cothrige > Patrick. S így lesz a leányból (ci) király (ri). Mindez a wikinél. The word "patrician" is derived from the Latin word patricius (plural patricii), which comes from patres, the plural of the Latin word pater ("father"). Celtic. "patro", atir, c.f. edrydd "home", szinte "putra". Hell called "put". Thus the word sanskrit "putra = son". Putri pedig kunyhó/hut. The verb "patal" means to "twist" in Hebrew. A párkák pedig fonták a sors fonalát, ami sokak számára fatalis volt.
Late Latin patriarcha (Tertullian), from Greek patriarkhes "chief or head of a family," from patria "family, clan," from pater "father". His-pallus - tűz templom?
*(Esti/a, (Ion. Ἱστίη), the goddess of the hearth, or rather the fire burning on the hearth, was
regarded as one of the twelve great gods, and accordingly as a daughter of Cronus and Rhea. Hes-tia was the goddess of domestic life.
Patria:
From patrius (“of or pertaining to a father”), from pater (“father”), ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *ph₂tḗr. Cognate with Ancient Greek πατριά (patriá, “generation, ancestry,
descent, tribe, family”) and πατρίς (patrís, “place of one's ancestors”).
Father:
From Middle English fader, from Old English fæder, from Proto-Germanic *fadēr (compare West Frisian faar, North Frisian faaðer, Low German Fader, Dutch vader, German Vater, Danish fader), from Proto-Indo-European *ph₂tḗr (compare Irish athair, Tocharian A pācar, B pācer, Persian پدر (pedar), Lithuanian patinas (“male animal”), akin to Latin pater, akin to Ancient Greek πατήρ (patḗr), akin to Armenian հայր (hayr), akin to Sanskrit पितृ (pitṛ, “father”)
Pathfinder: Pedar, Pater, Patria, Patriota, Patrona, Patriarch, Pathos, Path-etic, Patisszon, Patens, Patiens, Pattern, Paatikaa..
Sym-pathy = együtt-érzés. Apathya = Érzelem nélküliség.
A patria (haza, szülőföld) a holland nyelvben tuisland. Tíz, tiz tiszta víz... De honnét ered a "tiz/10" szavunk ?!
A varég, gót, krimean stb nyelvek "ti, tien, tiu" szava (10) illetve az újlatin nyelvek "diez, dis.." szava vagy az észak-afrikai "tiz-iri=hold-csillag". Bár egyenlőre a "tűz" szavunkat sem zárnám ki. Továbbá a cikk végén látható "ti=kéz" szó is alkalmas lehet. A román "patru=4". (So, the number “four” symbolizes the “unity” and “concord”. It is based on the belief the universe is made up of a combination of four eternal "elements" or "roots of all": earth, water, air, and fire.) Chandra nádi?
Patrol: From French patrouiller from Old French patouiller (“to paddle, paw about, patrol”) from patte (“a paw”). A "pat, pot=láb" származéka. De ide sorolják a félhold formájú (half Moon shape) "patkó" szavunkat is. "Pan Tal= Half-Moon", korean and "Pak-Tal tree =Sandalwood". Moon Jar (Tal-hang-a-ri). (Köze lehet Buddhához, vagy a többi kamennaja babahoz?)
Sanskrit vándor: paT {paTati}, to go , move. to be master, reign, rule, govern, control, own. falling; sin, wickedness. paaTikaa half moon stone at the entrance of a building or at the base or a flight of steps. (From Pali lang.) Vajon mi a kapcsolat a Pat-ika és a Kat-ika között?
Batoni is a Georgian word for "lord", or "master". It is derived from patroni.
Pathology: the science or the study of the origin, nature, and course of diseases.
Görög érme: Patraos . 335-315 BC. AR Tetradrachm (12.42 gm). Laureate head of Apollo right / Horseman riding down fallen warrior; EM monogram left. Sotheby?s, "Paeonian Hoard,"
Rao néhol király. De minek a királya a Pat-rao?
Pat Heung
Chinese temple. Patesi \papkirály, Pa*te"si\, n. [Assyrian.] (Babylonian Antiq.) A religious as well as a secular designation applied to rulers of some of the city states of ancient Chaldea, as Lagash or Shirpurla, who were conceived to be direct representatives of the tutelary god of the place. Ziusudra was his name, and like the present day Patesi Utu, he had worshipped the Igigi.
John Jamieson: A Etymological Dictionary of the Scottish Language.
Mithras
Mithras: is often depicted by two smaller figures, dressed like himself, bearing torches. These torchbearers are named on the monuments as Cautes and Cautopates. Porphyry (de Abstinentia, 4.16) states that the "Mithraic priests" were called ravens, but this is probably a confusion with the initiation grade of that name. Cautes and Cautopates, the celestial twins of light and darkness. Kutyavilág: From an Old Iranian point of view this °pates might represent either *pāta- “protected (by)” or *pati- “lord, master (of).” As for cautes, cauto-, it is tempting to understand the two names as deriving from a single epithet of Miθra attested in Avestan as vouru.gaoiiaoiti-; thus, Cautes would be a latinized form of a hypocoristic *Gauti of *(varu-)gau(yau)ti- and Cautopates, *Gautipāta/*Gautipati a secondary formation on *Gauti (Gershevitch, pp. 151-52). Another possibility is to derive Cautes from Median *kauta- “small, young” (cf. Mid. Pers. kōdag). Mithrász fáklyavivői. Cautes fáklyája felfelé, Cautopates fáklyája lefelé áll. Tán Cautes a napfényt, Cautopates pedig a holdfényt szimbolizálja.
God
Isten - Baga
Turkish took the title bäg, beg, and later bey; in early Turkish in Brāhmī script it was bhek, and in Byzantine Greek the Khazar title was written mékh. The form bägräk occurs in a Turfan Manichean source. In Arabic script the Turkish title was bag, baḵ, and bāk. (Korea Hongkongban?)
It is not likely that OIr. baga- derives from a word meaning god in IE., despite the occurrence of bogŭ “god” in the Slavonic languages (probably as a result of Iranian influence. Bogu-mell?). Etymologically, baga- “god” belongs to the verbal root bag “to distribute, allot” and may be equated with OInd. bhága-, a divine epithet probably meaning “dispenser; generous one,” beside which there exists also a second noun bhága- “distribution, allotted portion” equivalent to Av. baγa- “portion, lot,” Slavonic *bogŭ in derivatives such as ubogŭ “poor” (from “*portionless”).
Sanskrit
Turya: the fourth state of consciousness beyond the waking, dream and deep sleep states; the witness consciousness.
Samvit: Supreme consciousness. (Manysi "szemvíz".)
Buddhi: discriminating intelligence, the intellect, the discriminative faculty; from the root-verb budh, meaning ‘to enlighten, to know.’
Religions
The ancient Egyptians also had the legend of the "Tree of Life." It is mentioned in their sacred books that Osiris ordered the names of some souls to be written on this "Tree of Life," the fruit of which made those who ate it to become as gods.[12:3]
Among the most ancient traditions of the Hindoos, is that of the "Tree of Life"—called Sôma in Sanskrit — the juice of which imparted immortality. This most wonderful tree was guarded by spirits.[12:4]
Still more striking is the Hindoo legend of the "Elysium" or "Paradise," which is as follows:
"In the sacred mountain Meru, which is perpetually clothed in the golden rays of the Sun, and whose lofty summit reaches into heaven, no sinful man can exist. It is guarded by a dreadful dragon. It is adorned with many celestial plants and trees, and is watered by four rivers, which thence separate and flow to the four chief directions."
KELETI SZERTARTÁSÚ EGYHÁZAK híveinek száma
Alexandriai rítus 360 000
Egyiptomi (kopt) egyház 210 000
Etióp egyház 150 000
Antióchiai rítus 4 040 000
Malankár egyház 340 000
Maronita egyház 3 580 000
Nyugati szír egyház 120 000
Örmény rítus 270 000
Örmény egyház 270 000
Káld vagy keleti szír rítus 3 750 000
Káld egyház 340 000
Szír-malabár egyház 3 410 000
Bizánci rítus (görög katolikus) 8 437 300
|
Albán egyház 1 500
Bulgár egyház 22 000
Gör. katk. a volt Jugosz-ban 53 000
Görög-melkita egyház 1 189 000
Görög egyház 2 500
Fehérorosz egyház 5 500
Magyar görög katolikus 302 000
Olaszországi görög kat. 67 000
Román görög katolikus egyház 550 000
Orosz görög katolikus egyház 3 800
Rutén görög katolikus egyház 533 000
Szlovák görög katolikus 258 000
Ukrán görög katolikus 5 500 000
|
Kereszténység és buddhizmus. -
A buddhizmusban és a kereszténységben a következő kultuszelemek hasonlók:
1. a kolostori élet (szerzetesek, apácák, újoncok és felszenteltek).
2. a cölibátus,
3. a tonzúra,
4. a gyónás,
5. az ereklye-tisztelet,
|
6. az olvasó,
7. a templomtorony,
8. a füstölő
9. a harang használata.
Comparison Jesus (vízen járás, halak..) |
A cigányok indiai eredetének bizonyítékai:
1. A nyelv minden dialektusában megtalálhatók az ind eredetű szavak, perzsa, örmény, kurd, görög jövevényszavak mellett.
2. Pandzsabbal való rokonság. A hasonló arcvonás, a testalkat, a bőr jellegzetes színe, a szokások és hagyományok rendszere. A cigányok ősei, amikor elhagyták Indiát, még Káli istennőt imádták, majd a kereszténység befolyása alá kerülve Szűz Mária vette át ezt a szerepet. Siva isten jele a trushula, (a cigányban trushul =3 ágú szigony) Jézus keresztjévé vált.
("M" mtDNA és "H" y hg. Fura, de India kurava cigányait ott is "gypsy" néven emlegetik, s állítólag sok közöttük az "R1a" y hg.)
Nyesztor
A nesztoriánusok hozták létre - Edessza központtal - a szír-kháld (keleti szír) egyházat (és liturgiát). Ennek indiai térítési területén (Malabár-part) 525 körül létrejött az indiai Malabár egyház. A nesztorianizmus Sz.Mária Istenanyaságát vitatta, ezt a 43l-es Epheszoszi Zsinat ítélte el.
malabar vallás - bePALLIzták őket?
The contacts between Phoenicia and South India go back to second millennium BC. Jews came into contact with south India in the tenth century BC following the commercial enterprises of Solomon. They were following the footsteps of Phoenicians from the Tsur and Sidon. The king Hiram of Tsur, the contemporary of Solomon (972-932 BC) promoted international trade with South Indian Coast. Spices like pepper, ginger, precious gems, ivory, gold, peacocks, apes etc. were exotic attractions from South India.
The Roman army conquered Egypt in 30 BC and took over the control of international commerce through Egypt. 120 ships used to sail every year from Red sea to the Malabar Coast. Within 40 days the Monsoon winds brought them to the Coast. With the help of opposite Monsoons these ships used to return to Egypt in the same year. Coonan Kurisu (Bent Cross) Palli (Church) or Holy Cross church.
Mint látjuk, Nestor patriarcha nézetei Bizánctól Indiáig, Kínáig terjedtek. Csak északra és nyugatra volt tiltva az ideológia. S az un. avar vándorlás előtt már Közép-Ázsiában a nyesztorianus vallás dominál, pahlavi nyelvezettel. Európa északi területein természetesen a hun boncok laktak, akiket majd a megyer törzs táltosai váltanak le..:-).
Cross
The Coonan Cross Oath (Koonan Kurishu Satyam), taken on 3 January 1653, was a public avowal by members of the Saint Thomas Christian community of Kerala, India that they would not submit to Portuguese dominance in ecclesiastical and secular life. The swearing of the oath was a major event in the history of the Saint Thomas Christian community and marked a major turning point in its relations with the Portuguese colonial forces. The oath resulted in the excommunication of 54 years Roman domination started with the synod of Diamper in CE 1599 by the Portuguese and declaration of the sovereignty Malankara Church in 1665 AD, with Mar Thoma I.
Mind szent: "Mar" képek. ..és a veresegyházi asszonykórus.
Családi élet - Nyesztor eltörlése
Az a kísérlet, hogy megszabadítsák a malabár rítust a nesztorianizmus mindenféle nyomától, végül arra vezette Goa érsekét a jezsuita misszionáriusok segítségével, hogy összehívja a diamperi szinódust (1599), ami a latin szokásoknak a Tamás-keresztényekre való bőséges ráerőszakolásába fulladt. Körülbelül mindaz, ami megmaradt az eredeti rítusból, a szír nyelv volt, a zsolozsma és az eucharisztikus liturgia alapvető formája, amelybe sok latin elemet vezettek be. Csupán egyetlen anaforát, Addai és Mari anaforáját fogadták el, eltörölve mindenféle lehetséges heterodoxiát, és hozzáadva az átváltoztatás szavait a végén. Kovásztalan kenyér volt előírva az eucharisztiához és egyetlen szín alati áldozás. A szentségek megünneplése alatt egy szírre fordított, XVI. századi portugál Rituálét használtak. Továbbá bevezették a Pontificale Romanum egyik szír verzióját. A régi liturgikus könyvek kéziratait elpusztították, hogy megtiltsák azok használatát, és új naptárat adtak ki, hogy eltöröljék az összes nesztoriánus szentet. Jóllehet a szinódust hivatalosan nem fogadta el Róma, szabályait követték Indiában.
A szinódus döntéseivel való ellenkezés csúcspontját a Kunan Cross-ban tett ünnepélyes esküvel érte el 1653-ban, de sok lázadót fokozatosan meggyőztek, hogy változtassa meg gondolkodását. Azoknak a Tamás-keresztényeknek, akik elutasították, hogy engedjenek a latinizálásnak, végül sikerült kapcsolatba lépniük a szír ortodox Egyház pátriárkájával, aki elfogadta, hogy joghatósága alá vegye őket, és hogy püspököt adjon nekik, azzal a feltétellel, hogy ők viszont fogadják el egyháza teológiáját és liturgiáját. Ez alapozta meg a malankár rítust Indiában.
János pap országa
..s az apokrif Széth könyvében olvasható, hogy Jézus feltámadása után a keleti térítő úton lévő Tamás apostol keresztelte meg az egykori mágusokat. A latin hagyomány megőrizte még nevüket is: Gáspár, Menyhért, és Boldizsár.
Nesztóriusz tanait alapul véve már néhány évtizeddel a halála után létrejött az új és rohamosan terjedő szekta Szíriában és Perzsiában. Gyors terjedésére
jellemző, hogy már ugyanekkor, vagyis az 5. század végén Belső-Ázsiában is létrejött a mervi (Maru) és a herati (Hara) püspökség. Misszionáriusaik sokoldalú emberek voltak, ügyes kereskedőkként jól boldogultak, s mivel értettek a betegségek gyógyításához is, közkedveltek lettek a nomádok és oázislakók
körében. A belső-ázsiai nomádok első nesztorianus törzse a kereit volt, a róluk szóló első tudósítás a 11. századra nyúlik vissza, s a 13. században jegyezte le Bar Hebraeus.
St Thomas kereszt
Tyndis is of the Kingdom of Cerobothra; it is a village in plain sight by the sea. Muziris, of the same kingdom, abounds in ships sent there with cargoes from Arabia, and by the Greeks; it is located on a river, distant from Tyndis by river and sea five hundred stadia, and up the river from the shore twenty stadia. Nelcynda is distant from Muziris by river and sea about five hundred stadia, and is of another Kingdom, the Pandian.
The symbol of the Nasranis is the Syrian cross, also called the Nasrani Menorah Mar Thoma sleeba in Malayalam. It is based on the Jewish menorah, the ancient symbol of the Hebrews, which consists of a branched candle stand for seven candlesticks. (Exodus 25).
Sólyom
Asura, Asur, Ashur
ṛkite’. Rebus: pasra ‘smithy, forge’ (Santali)
2. śyēná m. ʻhawk, falcon, eagleʼ RV.Pa. sēna -- , °aka -- m. ʻhawk ʼ, Pk. sēṇa -- m.; WPah.bhad. śe
ṇ ʻkiteʼ; A. xen ʻ falcon, hawk ʼ, Or. se
ṇā, H. sen, sẽ m., M. śen m., śenī f. (< MIA. *senna -- ); Si. sen ʻfalcon, eagle, kiteʼ. (CDIAL 12674)
Rebus 1: sṭs
ḗnā -- , páti --
ʻgeneralʼ, Pk.
ṇ -- m.; M. śe
vaī
ṇ m. śe
vi
ʻgeneralʼ (CDIAL 13589). Rebus 2: ṇṇ
]
 A vas fiai
A vas fiai
Glyph: meṭṭu ‘foot’. Rebus: meḍ
‘iron’ (Ho.Mu.) dula ‘pair’ (Kashmiri); dul ‘cast (metal)(Santali).
Religion
Amma's Jayanthi (Birthday) - The day begins with a procession followed by a holy bath for Amma. After this Amma performs all the regular pujas. Special pujas and yagnas are also performed by the temple Priests on January 2nd and 3rd. At midday, on January 3rd, the celebrations are held in the Yagashala (Full Moon Hall) /Yaaga Shala= temporary settlement for conducting sacrifices/ located behind the Shanti Mandapam. The first meaning of the Sanskrit word Yagna is “sacrifice”. The second meaning is “offering to the Sacred Fire” (Agni). Yaga: there are 400 different types of Yagas (Fire Altar Ceremonies) and Yajnas. The three wicks in the lamp represent the three fires in the yagashala. Poya is the full-moon of Poson (June). Poya which in Sinhala means full moon.
Glyph: ‘foot, hoof’: Glyph: ‘hoof’: Ku. khu
ṭoʻ leg, foot ʼ,°
ṭī
ʻ goat's leg ʼ; N. khuṭoʻ leg, foot ʼ(CDIAL 3894). S. khuṛīf. ʻ heel ʼ; WPah. paṅ.khūṛʻ foot ʼ. khura m. ʻ hoof ʼ KātyŚr̥.
A vas
kolmo ‘three’ (Mu.) (This Kolmogorov 3 axioms); rebus: kolami ‘smithy’ (Te.)
Vikalpa: kaṇḍa ‘arrow’ (Skt.) ayaskāṇḍa
‘a quantity of iron, excellent iron’
मेंढा [ mēṇḍhā ] A crook or curved end (of a stick, horn &c.) and attrib. such a stick, horn, bullock. मेढा [ mēḍhā ] m A stake, esp. as forked. Vikalpa: kottaṉ a mason (Ta.) kotti pick-axe, stone-digger, carver (Ma.) Rebus: mẽṛhẽt, meḍ ‘iron’ (Mu.Ho.)
Turung nyelv
The Tur-ung? language (Tailung, Tairong, Thai: (pasa tai turung) is an extinct language formerly spoken in Assam.
Chandrakanta Abhidhan is an Assamese Language to English dictionary, the third one published. It contains 36,816 words and was originally compiled and published by Asam Sahitya Sabha in 1933.
Bokar, or Bokar-Ramo-Pailibo, is a Tani language spoken by Lhoba people in India and China. In India, Bokar dialect (Boga'er Luoba, Bokar gom) is spoken in Ramang village, Monigong Circle, Arunachal Pradesh (Megu 1990).
Dravidák
The word drāviḍa/drāmiḍa and its adjectival forms occur in Classical Sanskrit literature from the 3rd century bce as the name of a country and its people.
Drāviḍa as the name of a language occurs in Kumarila-Bhatta’s Tantravartika (“Exposition on the Sacred Sciences”) of approximately the 7th century ce. In these and almost all similar cases, there is reason to believe that the name referred to the Tamil country, Tamil people, and Tamil language.
Examples of these forms of suffixation include the series *kā-y ‘to burn,’ *kā-nk-u (intransitive verb) ‘to boil,’ and *kā-nkk-u (transitive verb) ‘to boil’ and the series *tir-i ‘to turn,’ *tir-u-ku ‘to roam,’ *tir-a-y ‘to roll,’ *tir-u-nt-u ‘to be changed,’ and *tir-u-ntt-u ‘to change.’
A myriad of other changes also took place. Middle Kannada changed South Dravidian *p to h at the beginning of a word; e.g., Old Kannada *pāl changed to hāl(u) in Middle and Modern Kannada.
For instance, Proto-Dravidian *uẓ-u ‘to plow’ became Kui, Kuvi, and Pengo ṛū- ‘to plow’ and Telugu ḍu-kki ‘plowing’; and Proto-Dravidian
*car-a-cu became Telugu trācu (mag edon?), later tācu, Konda srāsu, Kui srācu, Kuvi rācu, and Pengo rāc = kígyó (by loss of s-).
Proto-Dravidian *mar-u-ntu ‘medicine’ developed to Telugu mandu, Kannada mardu, maddu, Parji merd, and Kurukh mandar.
| gloss | Tamil | Kannada | Tulu | Telugu | Gondi | Kui |
| hand/ kéz | kai | kay, key | kai | cēyi | kai | kaju |
| man/ férfi,ember | avan | avan | āye | wāḍu | ōr | aanju |
Dravida nyelvek
More than a dozen Dravidian loanwords can be detected in the Sanskrit text of the Rigveda (1500 bce), including ulūkhala- ‘mortar,’ kuṇḍa ‘pit,’ khála- ‘threshing floor,’ kāṇá- ‘one-eyed,’
and mayūra ‘peacock.’
A number of place-names of South India cited by Pliny the Elder (1st century ce) and Ptolemy (2nd century ce) end in -our or -oura, which correspond to the place-name suffix -ūr ‘town’ from Proto-Dravidian *ūr. ..and *tur-a ‘to push’ became *tor-a in Proto-South and Proto-South-Central Dravidian.
Őskeresztények: - Kushan Carnelian seal representing the "ΑΔϷΟ" (adsho Atar), with triratana symbol left, and Kanishka's dynastic mark right. A kushan keresztes lovag lába kengyelben Krisztus
korában.
Kushan Empire
The nose ring, or Nath can be very elaborate, decorated with pearls or gemstones, and may be attached to the hair on one side of the head, with a chain
containing multiple drop-beads. In some regions the nose ring is never removed, becoming an enduring symbol of marriage. An black eye-shadow called Kaajal
is then used to accentuate the eyes.
Afrikai kapcsolat
There is DNA evidence to confirm the Kushite migration out of Africa. The Kushan-Yuezhi provide evidence of the perhaps the most recent movement of the
Kushites out of Africa. Some moved into central Asia and China and others moved into Japan. They are also called Gurjar. Gurjar is a reference to their
mercantilism and metal work.
Chinese
The Bogar form part of the official Lhoba nationality in China. In the 1990 census, only 2,312 Lhoba were counted. A 1987 study, however, reported 3,000 speakers of Bogar and 7,000 speakers of Yidu Lhoba. Some publications have incorrectly reported a population of 200,000 Lhoba in Tibet. The name Lhoba means "southerners" in the Tibetan language. The Lhoba are not the same group as the Lopa (Mustang) Tibetans of Nepal.
Merv
They stress the ancient origin of the city, and say in particular that the Merv citadel (Gyaur- Kala) was erected by Tahmorath, the third mythical ruler ( after, Kayomarth and Hushang ) of the pre - Achaemenian Iran and its old part - by Iskandar Zulkarnain - Alexander the Great.
Qalandars - Apokalipszis most
Dhungara-- The Singhâra nut
Dhurangi-- European
Khunnay-- House
Thokay-- Jungle
Thundi-- Girl.
The Narikurava or Narikorava or Kuruvikkaran (Kurava) are a community of Domba ("Indian gypsies") who reside in the Indian states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
Az apokalipszis 4 lovasa meghozza az összeomlást. Lásd a rómaiakat, amikor bevezették a zsidós tetrarchiátust...:-)
Tamil term Kuravar used by the early Alvars is corruption of "Kuraba", who were residents of this area and also of Kurnool, Mysore, Salem, coimbatore and the Nilgiris. He mentions the names of Kurubalakota, Kurubalpatti, Kuruba Nagalapuram, Kurumba Palayam, Kurumbapatti, Kurumbharhalli etc. in various areas.
Indian castes
There is some connection between Ambalakarans, Muttiriyans, Mutrachas, Uralis, Vedans, Valaiyans, and Vettuvans, but in what it exactly consists remains to be ascertained. It seems likely that all of them are descended from one common parent stock. Ambalakarans claim to be descended from Kannappa Nayanar, one of the sixty-three Saivite saints, who was a Vedan or hunter by caste. Tamil Kuruvi means small birds.
Úgy legyen! Ámen! Sri Lanka nyelvén äm=yes. Tamil: "nari=adult female/felnőtt nő". The kuravars, who are often called "gypsies" by people in Chennai and other parts of Tamil Nadu, and who are also called narikuravars. Nandooruthu meaning?
Harappa - Nyugat-Pakisztán nővérei
 Kelet-Pakisztán - Hét szél? Hét nővér
Kelet-Pakisztán - Hét szél? Hét nővér
The Seven Sister States, also called "Paradise Unexplored", are the contiguous states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura in northeastern India.
Tharan-Trieb Marianne: Harappa jelei megfejtve?
Az eredmény meglepő: a kézművesek szókincse minden mai indiai nyelvben az Indus völgyi kultúra idejében kialakult nyelvi kapcsolatokból származik. A bronzkorban az ötvözést feltaláló kézművesek írásrendszert is alkottak. A Meluhha kereskedelem pedig vitte az írást tengeren, folyón és szárazföldön mindenfelé. Ezen vonások közül sok közös az ugro-finn nyelvekkel is, mivel ezekben is a gyökök alkotják a nyelv fő alapelemeit, amelyekhez posztpozíciók, vagyis névutók járulnak.
Közös, hogy hiányzik belőlük a „birtokige” (have, haben), megvan a magánhangzó illeszkedés, a hangutánzó és ikerszavak sokasága. A valóságban több szerkezeti és hangtani hasonlóság van a szanszkrittamil- magyar, stb. között, mint az indoeurópai nyelvek között. A hegy – hármashalom – jele India különböző területein, különböző korokban: a legősibb jeleket a Bhimbetka barlangokban találjuk mint az emberi jelenlét legkorábbi nyomait Indiában.
A barlangok legalább 100 000 éve folyamatosan lakottak, a sziklarajzok 30 000 év óta készültek folyamatosan, és a legrégibb ábrázolások – vonalak, hullámvonalak akár 700 000 évesek is lehetnek. A halmokra rajzolt jelek a hegyekben talált fémekre utalnak.
Dravidák az Indusnál
Michel Danino* rajzolt egy szép térképet, ami azért nem olyan színes, mint a mi finnugorászainké volt. Látszik, hogy a dravidákat az Indus felől szorították a szubkontinens déli részére. Mint írja, a proto-elamita és az indus script feltűnően hasonló. Csak az nem passzol, hogy a Harappa kultúra a bolygónk kultúráját évezredekkel megelőzte, s annak nyoma sincs Elam területén..
Afghanistan
After the Indus Valley Civilisation which stretched up to northeast Afghanistan, it was inhabited by the Aryan tribes and controlled by the Medes until about 500 BC when Darius the Great (Darius I) marched with his Persian army to make it part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Ai-Khanoum or Ay Khanum (lit. “Lady Moon” in Uzbek, possibly the historical Alexandria on the Oxus, also possibly later named اروکرتیه or Eucratidia) was one of the primary cities of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom.
Ai-Khanoum was one of the focal points of Hellenism in the East for nearly two centuries, until its annihilation by nomadic invaders around 145 BC about the time of the death of Eucratides.
Virgin
Seven sisters of India: The Seven Sisters of India are relatively untouched, unexplored and isolated states of north east India. North East states are heavily forested and land of tribes peoples. These states are full of natural beauty,exotic places and wide variety of beautiful wild animals like rhinoceros, elephants and numerous species of birds.
Heten
Assam is mentioned in epics like Mahabharata as it was inhabited by Aryans belonging to warrior and priestly classes who migrated to Assam very early.
Syl-hette: Hette a bangla nyelvben "öregasszony" jelentésű. Sylheti written with Bengali script, syl-Beng, Sylheti [syl]. Alternate names: Sileti, Siloti, Sylhetti, Sylhetti Bangla, Syloti, Syloty, Srihattia. In the district of Sylhet there are three ancient stone images of Vasudeva worshipped in three different places.
Dialect - A sylheti név változatai.
Purulia
Several rivers flow across Purulia. Among these Kangsabati, Kumari, silabati(silai), Dwarakeswar, Subarnarekha and Damodar are the important ones.
Hill: mountain sylsiit-em
Meluhha
The word which signifies a fire-altar is kanda (Meluhha~Santali) The narrative is a prayer to fire-god. Karandi fire-god (Munda, Remo). Rebus:
kole 'temple'. Persze, mert a "kole=templom" azért az "isha-kole" még nem tűztemplom..
A vesta
Avestan vis- “village,” corresponding to Avestan v?r?z? na- “clan”; Avestan zantu- “district”; and Avestandaxiiu-, dańhu- (Benveniste, 1932; idem, 1938, pp. 6, 13; Thieme, pp. 79ff.; Frye, p. 52;
From the meaning of Old Persian dahyu as “limited territory” come Middle Persian and Pahlavi deh “country, land, village,” written with the ideogram MTA (Frahang i Pahlawig 2.3, p. 117; cf. Syr. mata), and Manichean Middle Persian dyh (MacKenzie, p. 26). At times the Avestan use is reflected in Pahlavi deh, but already in Middle Persian the meaning “village” is well documented; it appears again in Persian deh.
Maha barata - Nagy India
Rebus readings of Meluhha hieroglyphs on the following relief from Ashur point to the catalog of metalwares of the bronze-age Meluhhans who had settled in Ashur. The link of Sumer with Ara??a (known as La?a, a Meluhha speech area) has been detailed at and related links.
kola ‘woman’ Rebus: kol‘ 'smithy, working in iron’
The Dravidian Languages. szerző: Bhadriraju Krishnamurti.
English- brahui- Dravidian
Bow- bil- vil/bil
Milk- palh- pal
Scorpion- tel- telu/chelu
Son- maxh- maga
Gene
Haplogroup M17 is regarded as the Aryan stamp on Indian populations. An extensive 2003 study conducted on 1000 Indians stressed that M17, which is found frequently in Central Asia, is present in two Indian aboriginal tribes.
The Soviet Decipherment of the Indus Valley Script: Translation and Critique Szerkesztette: Arlene R. Zide,Kamil V. Zvelebil
Az oroszok is megfejtették a harappai írást.
Not rebus
All the Indo-Aryan languages have at least a word close to the Early-Aryan word kumbha or kalasa which means vessel. In Telugu it is called kundalu, in Tamil it is kutam, in Bengali it is kalsi. Moreover in Satali the word kan.da means ‘a pot of certain shape and size’. In Pali also there is a word kuta which possesses the same meaning.
Shem fiai
However, dual origins or an Indian admixture is also possible given the genetic study by Sengupta et al. (2006), found the Kalash to comprise high frequencies of Haplogroup L3 (25%), R1a (20%), H1* (20%), Haplogroup G2a (20%), R* (5%), J2a and J2b2 at (5%) each. Haplogroup L originates from prehistoric South Asia…See Sengupta, S et al. (February 2006). Maradék és egy olasz Kínában, akinek írása veszélyes, mert sok igazság is van benne, ami elfedi a hamisat!
Szimbólumok
Could the crescent-on-arches mark have been used to indicate descent from moon, or descent from Chandragupta (the first Mauryan emperor; Chandra=Moon)?
Chandragupta Maurya (3rd BC.)
Wiki Info - The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in ancient India, ruled by the Maurya dynasty from 322–185 BCE. Originating from the kingdom of Magadha.
Indus Valley
The great stupa of Sanchi was one of eight stupas that originally contained the Buddha's ashes. Ashoka gave the great stupa a major overhaul and also took most of the ashes out of the original eight stupas and distributed them to thousands of other stupas throughout his empire. Stupas can come in many sizes, are solid and each incases an icon of Buddha inside it. Stupas can be small enough to carry and move around or they might be massive buildings (with no interior.) Buddhists circumambulate around stupas clockwise, chanting prayers.
Az Indus kultúra sokat idézett képe a szakállas férfié, akinek mellén a ruhát három levelű mintázat díszíti. The trifoil pattern on his robe can represent leaves, or a religious symbol like the Trinity.
"Triglav"
The Tridevi (English: three goddesses; Sanskrit: ???????? tridevi) is a concept in Hinduism joining the three consorts of the Trimurti, or the Great Trinity. This union is personified by the forms of the Hindu Goddesses, Saraswati, Lakshmi, and Parvati. In Shaktism, these deities are the manifestations of Shakti, the Divine Mother.. Ilyen hármasság a Buddha-Visnu-Siva istenségek is.
3 istennő
In South Arabia the moon-god Hubal was accompanied by the three goddesses: Uzza the youngest, Al-Lat "The Goddess" and Manat the Crone, the three cranes. The Celtic triple spiral or triskele symbol is sometimes called the spiral of life and was found in the Newgrange site from the Bronze Age in Ireland. The triple spiral is an ancient symbol of Celtic beliefs, and was used consistently in Celtic art for 3 millennia. The Celts believed that all life moved in eternal cycles, regenerating at each point. Celts also believed that all important things came in three phases; for example: birth, death and rebirth and mind, body and spirit.
3-as kunhalom Hármas halom Vaskút határában
Nyugati Ghatok - pávák, templomok. Görögszéna: arab "hulba", francia "fenugrec" (Middle English fenigrek, from Old French fenegrec, from Latin fénugraecum, from fénum Graecum : fénum, hay) és a tamil "venaya kirai".
(Kiran is of Hindi and Sanskrit origin, meaning "beam of light".) The Ethiopian spice mixture berbere (see long pepper) contains small amounts of fenugreek.. Berbere can be made into a paste with water, wine or mead (tej).
Ethnologue: p. 438 (Chin, Falam (Hallam Chin, Halam, Fallam, Falam); spoken in Burma, India, Bangladesh) p. 472 (Halam, an alt. term for Falam Chin, is distinct from Halam, a dial. of Kok Borok, spoken in India). Forgotten: " cha " in Aimol, Anal, Kolhen, Lamgang, " shak " in Chiru, meaning '"' to eat."
Tribes
The goddess of Halba tribe is Ma Danteshwari. The language of Halba tribe is "Halbi", which is combination of Hindi, Chttisghari, Oriya and Marathi.
India nyelvei
South Asian languages belong to four major language families: Indo-European (>Indo-Aryan), Dravidian, Austroasiatic (>Mon-Khmer and Munda), and Sino-Tibetan (>Tibeto-Burman).
Monostor
Bagaya is a Burmese approximation of Mon language phea kao kih, literally "starflower monastery."
Pali: moon stone: (f.) paa.tikaa. month: (m.) maasa. monthly: (adj.) maasika.
stone: (f.) silaa. blue jay: (kék szajkó, mátyásmadár) = kikii.
Kocsi, szekér: For instance, gadi in Sindhi and gari in Hindi is gadai (“a cart”) in Pashto

Edd - ečem ičen! (ечемичен)
Vedic pa- ‘drink’ and Avestan fra-xvar- ‘consume’ allow their object argument to be alternately expressed by the accusative or the genitive (cf. also Vedic ad- ‘eat’. Buryat "ede = food". Klasszikus mongol: "idegen=food".
svadha�m pipaya subhú ánnam atti /
wantonly swell-PRF strong-ACC food-ACC eat-PRS
‘He has swollen wantonly. He eats excellent food’ (Rigveda II 35.7)
a. pácanti te v��abha�m� átsi té�am
cook.PRS you.DAT bulls.ACC eat.PRS them.GEN
Edible kicsit részletezve.
Caitiya - Árkádok alatt
Terminus
Site rupestre de Bhaja : caitiya (temple) comportant un stupa.
Sinhala
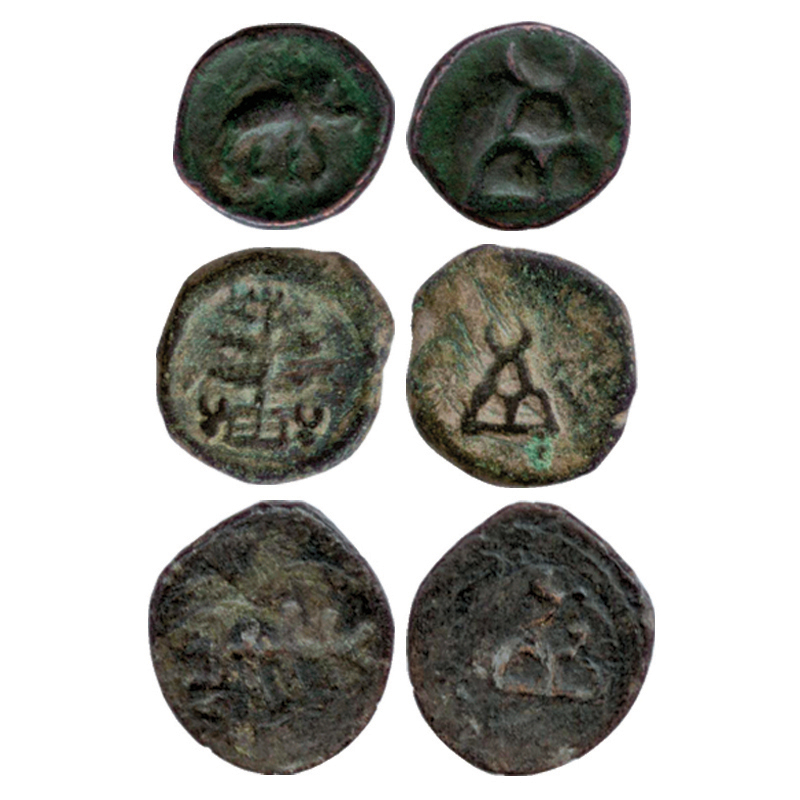
Számok Ceylon (Si-lon) ókorából. A pénzérmén itt is látható Chandragupta 3 halma. Sinhala pénze. Feltűnik rajta a 3 hegy és a 3 pont. Gandhara coinage.
Whole caust
A Comparative Dictionary of the Indo-Aryan Languages. szerző: R. L. Turner:
caitiya, caitya: "relating to a funeral pyre", m.n. 'funerel monument, sacred tree'. Pa cétiya 'sepulchral monument', Pk céia m.n. OG. ceiya, cei m. "shrine"; OSi (Brähmi inscr.) ceta, ceya, Si. säya "heap of wood, funeral pyre" H. Smith JA1950. 207.
Aesthetics in Performance: Formations of Symbolic Construction and Experience. szerző: Angela Hobart,Bruce Kapferer
Practices centering on the key objects of Buddhist worship as well as thr objects themselves (e.g. the Buddhist statue or the central Buddhist edifice, the magnificent aesthetic , perhaps perfect, architectural form of the Buddhist dagaba [stupa, caitiya] express a simplicity and supression of aesthetic excitement. Crescent: A "Western satraps" nagy városa "Ujjain". The Western Kshatrapas were Scythian (Saka) people who ruled a substantial kingdom that encompassed much of modern-day Gujarat and Maharashtra and some adjacent areas (see map in Figure 1). In the table, the column marked K/M is to indicate the title of the king. “K” means coins of that king are known with title kshatrapa only, “M” means coins are known with title mahakshatrapa only, and “K,M” means some coins are known with the kshatrapa title and others with the mahakshatrapa title for that ruler. Az "Ujjain szimbólum" egy egyenlő szárú kereszt, a négy végén egy-egy körrel. A körökben néha egy-egy kisebb kör van, esetleg egy hakenkreuz.
According to the Hindu tradition Ganga is also inseparable from the Shiva emblem as the crescent moon. Wherever there is a Siva emblem, Ganga must co-exist.The practice of taking seven steps- known as Saptapadi in Sanskrit- is associated with Hindu marriage ceremony and fire worship. The culminating rite in a Hindu marriage enjoins upon the bride and groom to go round the sacred fire four times (but misunderstood by many as seven times). Since "Makha" means fire, the seven circumambulations also prove that Mecca was the seat of Indian fire-worship in the West Asia.
Stupa
This term ‘cetiya’ was adopted by the Buddhists to mean a stupa, as cetiya and caitiya).
 Nagy utazás
Nagy utazás
Other symbols include the elephant with Bodhi tree, a three-arched hill (caitiya) and on the reverse a throne, and a nandipada (early Aum symbol as in the peacock wings) with three-arched hill in lower center [xvii].
The akhet contains the sun at dawn rising between two hills. On this fresco, a scarab beetle, a sign of rebirth, is present in the rising sun. All are contained inside the boat of the dead. Therefore, the Hindu three-arched hill may be synonymous with the dawn of the Egyptian akhet.
Három halom
AR Drachm. Reverse: Three-arched hill (chaitya), crescents and star above, river below; Brahmi legend. A mohamedánok előtt fél évezreddel a hármas halmon a félhold szimbólum. (Mintha 3 Nap és egy félhold lenne a szimbólum. ABC csillagok?)
A diadalív árnyékában
The triumphal arch of Constantine epitomized the history of the arch. The three-fold (openings) and the fourfold (the columns) are jointed together in the first impression of the structure (drawing by Marten Kuilman).
Malwa Through the Ages, from the Earliest Times to 1305 A.D. szerző: Kailash Chand Jain
But on the coins of the Sätavähanas, the hill is three-arched. Thus Chashtana was the originator of six-arched hill, and afterwards it was adopted by the Sätävahana ruler, Sri Yajña Sätakarni.
Wiki pénz
The Local silver punch-marked coins, included in the Bhabhua and Golakpur finds, were issued by the Janapadas and were in circulation during the rule of the Brihadratha Dynasty which was succeeded by the Magadha empire founded by the Haryanka dynasty in 684 BCE; these coins show four punch-marks - the sun-mark, the six-armed symbol, arrows (three) and taurine (three) which were current even during the rule of Bimbisara (604-552 BCE). Ajatasatru (552-520 BCE) issued the first Imperial coins of six punch-marks with the addition of the bull and the lion. The successors of Ajatasatru who ruled between 520 and 440 BCE and the later Shishunaga dynasty and the nanda dynasty issued coins of five symbols – the sun-mark, the six-armed symbol and any three of the 450 symbols. The Maurya coins also have five symbols – the sun-mark, the six-armed symbol, three-arched hill with crescent at top, a branch of a tree at the corner of a four-squared railing and a bull with a taurine in front. Punch-marked copper coins were first issued during the rule of Chandragupta Maurya or Bindusara.
 Shungas
Shungas
"Later Sunga Kings - 1/2 Karshapana Circa 150BC-100AD. 2.56g. Obv: Cross, three arched hill and railed tree. Rev: Elephant standing left, cross and single arched hill above". Kaushambi region, Mauryan Copper 1 Kakani (c. 300-200 BC), 3.02g, an Elephant looking left, three arched hill on rev., A "pana" pénz volt..
Thai language
daao =star; a non-planetary celestial body; spot. jan =the Moon. ban chaa =to command; direct (Pan-csao?). boon =holy; virtuous; pure; sacred. meet = knife. suun =zero; the number or quantity zero. saam =three; the number or quantity three. (szám a hakka és a koreai nyelvben is 3.) see =color; colors; paint. Naprendszer : loak= Föld/Earth. A "lakh" a számok helyiértékét is jelenti. Lak sip = tizes helyiérték. A "sip" az Korea felé is "sip". A százasok "lakása" a lak roi. Csúnya szavak thai nyelven: whore=gah-ree; ugly=kee ray.
Árják és dravidák
The Hill Madia are an endogamous ethnic group, conventionally called a tribe, belonging linguistically to the Central Dravidian group of central India. They are alternatively known in the literature as the Hill Maria, the Madia or Maria Gond. Madia:
kÃmlŒ ork ÂG itÀ
kÃmlŒ or-tœÉk ÂG i-t-tÀ
Kamli those.m-DAT water to.give-PAST-3NS
Kamli gave them water.
Indián törzsek - Maria országa
The Madia who live in Abhujhmad hills or known has Bada. The Gonds are mainly divided into four tribes: Raj Gonds, Madia (Maria) Gonds, Dhurve Gonds and Khatulwar (Khutwad) Gonds. According to them every hill, river, lake, tree is also inhabited by a spirit. Hakka means annual haunting festival in tribal Gondi language and ‘Abujhmad’ means unknown hill. India népe állítólag 444 nyelvet beszél. A törzsi népek fő tápláléka régen a "madia" (durva köles) volt, amit napjainra a "rizs" váltott fel. Hasonló nevű növény egy margaréta féle.
Egészségügy
A Gond törzsek vércsoportja: "0" > 38,4%, "AB" > 6,8%, "B" > 21,5% és "A" > 33,3%, Rh negatívak aránya 0,5%. Kiemelkedő arányban (22,4 %) fordul elő a sarlós vérszegénység soraikban.
Origins of Telugu Script
Dél-India nyelvei - a konkáni kivételével - a dravida nyelvek közé vannak sorolva. Az Indus-völgyi civilizáció írásos emlékeit itt egy proto-dravida nyelvnek aposztrofálják. Mohenjodaro és Harappa ásatásainál cca 400 "írásos emlék" került elő, melyeket többen megfejteni vélnek.
satavahana-dynasty
Their coins also display various traditional symbols, such as elephants, lions, horses and chaityas (stupas), as well as the "Ujjain symbol", a cross with four circles at the end. The legendary Ujjayini Emperor Vikramditiya on whose name the Vikram Samvat is initiated might be Satakarni II a Satavahana emperor as the Ujjayini symbol also appeared on the Satavahana coins.
Andhras
The Satavahanas were, for some time, vassals of the Mauryan Empire. Mauryan Emperor Asoka the great (reign: 269-232 BCE) and the rise of Buddhism played stellar roles in championing this spread of writing.
Govinda = Govu + Vinda : String that ties the cow
The moon (nichaya) amongst the Milky Way (thaaraka) of the devas (amara). Karpaka tree (kumuda hitha) to the devas. Blemish less (paripurna), sinless (anagha) one.
Aryan invasion
The Arians had a god of fire they called Agni. To the Arian's, Agni "was" fire, and they believed that Agni hungrily devoured the animals that they sacrificed in their rituals of burning. These sacrifices were performed by priests to obtain from their gods the gifts of children, success in war, wealth, health, longevity, food, drink or anything else that contributed to their happiness.
A Grammar Of The Hindoostanee Language John Borthwick Gilchrist
Chand=Moon. Chandee=silver. Nud=river. Nudee=rivulet. Gunga=river. punyla=watery. Hura-fa=green-ish. Bagh-ban=gardener. dur-ban=door-keeper.
Bű bájos
The mediators between spirits and humans in the rituals consist of two types. The first type, called pātri (Plate 1), darśan, or māni. Pātri means container, darśan means apparition, and māni means vehicle.
Devas are personified gods and goddesses enshrined in temples and shrines. The ritual site is mainly called mādu (māda).
Bhūtas include spirits of the forests, trees, animals (pig, tiger, boar, ox, snake), heroes who have died unnatural deaths, and people who have died from social injustice. Non-Brahmans worship them at the stāna (Bhūta stāna). In the case of Koti Chennaya, the ritual site is called with a special name, garadi (garodi).
The famous sacred places are: (1) Balnādu in the Puttur sīme; (2) Kepu in the Vittala sīme; (3) Paivalige in the Kumbla sīme; (4) Uliya in the Someśvar sīme; and (5) Balthila in the Mogranādu sīme.
Kusunda - will be a ‘barren’ language without its own cognates for objects such as: *ing (sun), *ngsa (fish), *uyu (blood), *gepan (language), *un (trail), *langhai (village), *suta (thread), *mucha (banana), *kakchi (crab), *tu (snake), "trail=ung" etc.
Santhali "Moon/Hold=Nydachado"; Sun/Nap=seingchando. "Eye/Szem=medh". Hand/Kéz=ti.
Indonezia - Timor
Bunaq nyelven az asszony/woman pana és a férfi/man "mona". A Hold az Hul. A Bunaq kemak neve Mgai. (PAN: lengyel ÚR, görög ŐR, Oporosz TŰZ, Indiai VÍZ egy-két nyelven LÁNY/ASSZONY. Panni > Fanni?)
Balochi language - cserkész
Bal. čar (r) “turn/move” ( AV. čara- “move”- Parth. Čar “graze”†
jan-† / jat “strike” (Av. Jan-, Np zan-/ zad, Parth žan-/ žad), jan “woman, wife”(Av. Jinni-, NP- zan
Zān- “know”(Av. Zanā-, NP dān-/dānist, Parth. Zān/ zānād), zāmāt “son-in-law”(Av. Zāmātār-, NP dāmād);mazan “big”(Av. Maz-, MPM mazan “monster”, OInd. Mahant-),mēz “urinate”(Av. maēza§-, NP mēz/ mēzīd.
Pesti István 2019 szeptember
Linkek:
A kicsik
India kapujában
A nagy barát
India hátsó udvara
Idegenek India kapujában
Nyitóoldal
 Kelet-Pakisztán - Hét szél? Hét nővér
Kelet-Pakisztán - Hét szél? Hét nővér A vas fiai
A vas fiai

 Nagy utazás
Nagy utazás Shungas
Shungas