|
|
|
 A legkorábbi indián állam: Kutai
A legkorábbi indián állam: Kutai|
Tocharian = ku Macedonian = kuche Urdu = kutta Bengali = kutro Gujarati = kutto Nepali = kukur Assamese = kukur |
Quechua: Curi Maori: kuri Bengali: kukur Boszniai. kucska Bulgar: kucse Estonian: koer Ógörög: kuon/kion Rohingya: kutta |
Gujarati: kutri Hindi: kuttä Magyar: kutya Hittite: kuwas Héber: kélev Kurd kumanchi: kücs proto-australian: gudaga |
Cornish = ky? Moldavian = kyne Bugotu = aku Finnish = koira Tatar = et Pahlavi = en Slovak = pes Irish = madra |
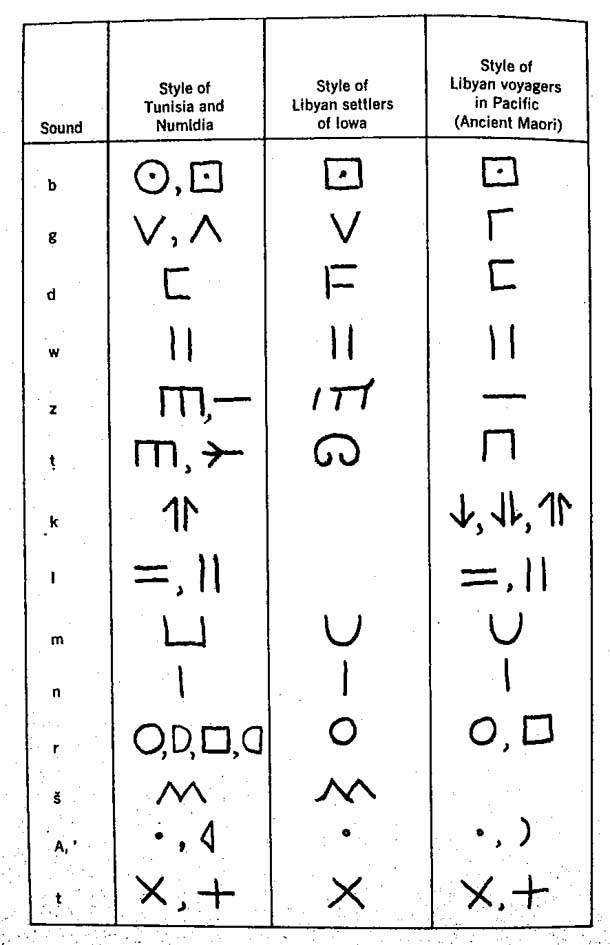 MAORI
MAORI  "The technicolor Waiotapu is a geothermal wonderland". "Waiotapu means Secred Water. 'Wai' means water in Maori, and ‘tapu’ is derived
from the Sanskrit word 'tapa' (Holy Abstinence, Penance), which got changed into 'Taboo' in the Polynesian languages. So, Waiotapu can be translated as “Taboo Water” (‘Tapojal’ in Indian languages), which also means “Sacred Water” reserved for God’s worship.
"The technicolor Waiotapu is a geothermal wonderland". "Waiotapu means Secred Water. 'Wai' means water in Maori, and ‘tapu’ is derived
from the Sanskrit word 'tapa' (Holy Abstinence, Penance), which got changed into 'Taboo' in the Polynesian languages. So, Waiotapu can be translated as “Taboo Water” (‘Tapojal’ in Indian languages), which also means “Sacred Water” reserved for God’s worship. Maori szavak:
Maori szavak:
|
|
|
MADURA |
 Ókori Ázsia:
Ókori Ázsia:
 Történelem előtti kapcsolat Amerikával:
Történelem előtti kapcsolat Amerikával: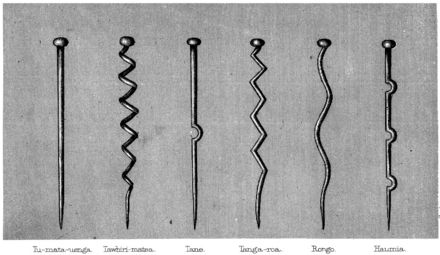 JELLEMZŐK:
JELLEMZŐK:
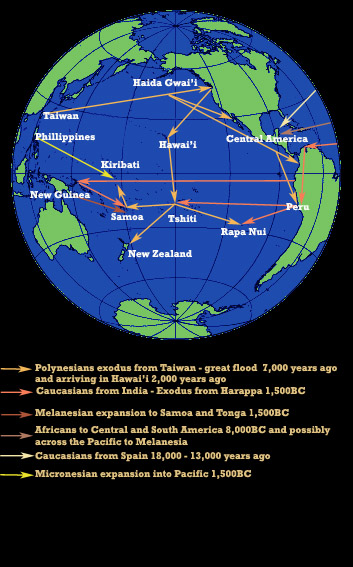
 ..Kiribati legends speak of an ancestral link to the 'Red Men' of Samoa, men who would raid islands and kill hundreds of victims as offerings to their gods once back in Samoa...
..There seems to be significant evidence to suggest that a number of different groups of these Caucasians entered the Pacific from America at various times. The Lapita people being the first, arriving as early as 1,900BC with a second wave arriving around
1,500BC...
..Kiribati legends speak of an ancestral link to the 'Red Men' of Samoa, men who would raid islands and kill hundreds of victims as offerings to their gods once back in Samoa...
..There seems to be significant evidence to suggest that a number of different groups of these Caucasians entered the Pacific from America at various times. The Lapita people being the first, arriving as early as 1,900BC with a second wave arriving around
1,500BC... A polinez betelepülésre több elképzelés született. A "lassú betelepülés" Melanézia felöl viszi a polinézeket Taiwan szigetére 6000 évvel ezelőtt. A problémát az okozza, hogy a melanéz nyelv hasonló DK-Ázsia nyelveihez. A melanézek ráadásul sötét bőrűek és göndör hajúak, akiket Nagy Emberek irányítanak. A polinézek világos bőrű, egyenes hajú nép.
A "gyors betelepülés" magyarázná a hasonlóságok hiányát, de nem ad választ a Lapita kerámia eredetére. (Amit polinez készítésűnek vélnek Bismarck-szigetek körül.)
A polinez betelepülésre több elképzelés született. A "lassú betelepülés" Melanézia felöl viszi a polinézeket Taiwan szigetére 6000 évvel ezelőtt. A problémát az okozza, hogy a melanéz nyelv hasonló DK-Ázsia nyelveihez. A melanézek ráadásul sötét bőrűek és göndör hajúak, akiket Nagy Emberek irányítanak. A polinézek világos bőrű, egyenes hajú nép.
A "gyors betelepülés" magyarázná a hasonlóságok hiányát, de nem ad választ a Lapita kerámia eredetére. (Amit polinez készítésűnek vélnek Bismarck-szigetek körül.) Újra és újra felmerül a kérdés: honnan származnak a polinéziaiak? Tudósok úgy vélik, a rágcsálók adhatják meg a választ. A legtöbb kutató úgy véli, a polinéziai népek az úgynevezett lapita kultúra leszármazottai. A lapiták mint egy 3500 évvel ezelőtt tűntek fel az óceániai szigetvilág nyugati részén.
Újra és újra felmerül a kérdés: honnan származnak a polinéziaiak? Tudósok úgy vélik, a rágcsálók adhatják meg a választ. A legtöbb kutató úgy véli, a polinéziai népek az úgynevezett lapita kultúra leszármazottai. A lapiták mint egy 3500 évvel ezelőtt tűntek fel az óceániai szigetvilág nyugati részén.  PÁPUA NYELV
PÁPUA NYELV
 Linkek a pápuák és környékbeliek nyelvéhez:
Linkek a pápuák és környékbeliek nyelvéhez:|
kiel=sail kiwaar=cassowary kongkong=small banboo gong saab= rubber tree saam= sky sar= white sug= to bathe tan= earth, ground |
tol=three ur=steam uz= to swim waag= hand drum yaaw= fire asur= blood gar= to bite maan= bird |
Pesti István
| Nyitóoldal |