A történelemből tán Róma a legjobban megkutatott rész. Nehéz új dolgokat találni...
Italy 8.
Fasti körkép
Saturnalia
Szaturnusz a földművelők istene volt. Érthetetlen is számomra, miért télen ünnepelték volna, hiszen a munkák kezdetekor vagy végén van értelme egy mezőgazdasági ünnepnek, nem a tél idején. A saturnalia minimum 3 napos, de adott esetben egy hetet is meghaladó ünnepségsorozat. Kezdődött állítólag december 17-én Saturnus ünnepével, majd folytatódott 19-én felesége, Opali tiszteletére tartott ünneppel, amelyet a 22-én kezdődő Sigillaria követett.
E során készült ajándéktárgyakkal lepték meg a téli napforduló idején a gyermekeket - de már csak a császárkortól kezdődően. A Saturnus egyesek szerint maga a Sátán. Ismert, hogy eskütételkor a mutatóujjunkat (jupiter/jutalmazó hatalom) és a nagyujjunkat (Saturnus/büntető hatalom) feltartva mondjuk el a szöveget.
Sosigenes előtt nem napévben számoltak a rómaiak. Vagyis, a december 25 csak véletlenül eshetett a téli napforduló idejére egy holdjárás alapú naptári rendszerben. Sosigenes előtt is 12 hónapos volt az év Rómában. Csak nem pont 365 napos. A szaturnáliákat ősi ünnepnek írják le, vagyis feltehetően Róma korai idejéig nyúlik vissza Szaturnusz megünneplése, de a Julián naptár bevezetése után lehetséges csak a napfordulóhoz kötni. Ott is csak úgy, hogy december 25 minusz egy hét. Mert a dec.17-én kezdődő 3 napos ünnep nem éri el a dec. 25-i Karácsonyt. Márpedig, ha hamisítás esete nem forog fenn, akkor Aurelián császár idejében a napforduló, Mithrász születésnapja - december 25-ére esett. A julián naptár bevezetése előtt élt Catullus is említi a saturnaliát, de idejéről nem szól.
Hahn István naptárai:
Ezért Rómában vidám hangulatban üdvözölték az újévet, hogy az egész esztendő ugyanígy teljék el. Az emberek édes ételeket, mézet, datolyát, aszalt fügét fogyasztottak, pénzzel és más figyelmességekkel ajándékozták meg egymást. A frissen hivatalba lépő magistratusok jelképesen ezen a napon kezdték meg működésüket a nyilvánosság előtt. A császárkorban ezek a szokások tovább terebélyesedtek. A császárok – akárcsak a mai államfők – a Kalendae Ianuariae napján fogadást tartottak, híveiket megajándékozták, a főváros lakosságának pénzt és élelmet osztogattak, katonai díszszemlén vettek részt. Az újév ünneplése fokozatosan magába olvasztotta a korábbi, hasonló hangulatú Saturnalia (december 17–23.) és azt követő Compitalia ünnepeket; ez utóbbinak az idejét évről évre külön hirdették ki.
Mivel lunáris? év volt a köztársasági Rómában, így a Szaturnália ünnepek vagy a december 17-hez köthetők, vagy a napfordulóhoz, de egyszerre a kettőhöz semmiképpen sem. S egy holdnaptár szerint élők miért is kötötték volna a Naphoz az évzáró ünnepüket? A julián naptár bevezetése után természetesen már lehetett a napfordulóhoz és egyben fix dátumhoz kötni egy ünnepségsorozatot. Állítólag Augustus császár kivett egy napot februárból, s azt az augusztus hónaphoz toldta. Ez által a naptár egy napot csúszott, s mint Ovidius említi, március 26-ra került a tavaszi napéjegyenlőség.
Sa=hely, turn=fordul > Saturnalia?
saturate= telít, átitat (angol)
WordRef
Teletölt, hogy a tartalom szinte áttüremkedik a tartály szélén. Átázik, átnedvesedik, átitat. Sapienti sat.
Satyr < görög "szaturosz" erdei isten (Silvanus). Rejtőzködő? Lappangó: Legends state that Saturn was forced by Zeus to become LATENT wich prompted him to seek refuge in LATIUM. Regarding "new beginnings", JANUARY in Greek was "GAMelion" which was a popular month for weddings or "matrimonial beginnings" ( perhaps this inspired Gregor Mendel to name fertile cells as "GAMetes"). JUNO, the daughter of Saturn also know as LUA was loose and dissolute and got LUES or sy-philis. Közösülés: the date related to the CYCLE OF THE MOON and SUN formerly know as "COPULATION" POINT reflecting SPRING or BIRTH OF NEW LIFE or PRIMA VERA. [FIRST TRULY]. A szifiliszt egyesek szerint Haitiről hozták Kolombusz katonái. Mások szerint a betegség neve "brit kór" Haitin a behurcolóik után.
Primavera
(Az első zöld megjelenése)
Nyári úticél: Aesti. Vagy szerelem első vérig. A halak szaporodása is korrelációt mutat a Nap és a Hold állásával. Verres meg kandisznó, verpa pedig himvessző.. Han dynasty performed sexual intercourse as a spiritual practice, called Héqi. Verra = war/háború. A "mesa verde" pedig zöld asztal.
Tavaszünnep = primavera. Az ókori népek tavaszünnepének, főleg a római szaturnáliá-knak hagyományaiban gyökerező, de a germán Hold s a szláv Perchta ünnepével is megtetézett szokás- és hagyománykör az európai népeknél továbbélt. James George Frazer: "when the Roman year began in March the Saturnalia was held in spring".
Polsko Węgierska Encyklopedia
Saturnalie, Saturnalia [w starożytnym Rzymie: święto ku czci Saturna] – (hist) szaturnália; elfajult, vad mulatozás, kicsapongás (eredetileg
Saturnus ókori római isten tiszteletére rendezett örömünnep a tavasz kezdetekor)
Pünkösdi király (ilyesmi volt a dictator is)
Az ókori Rómában a téltemetés-tavaszvárás jegyében álarcos felvonulásokat, zenés táncmulatságokat rendeztek, úgynevezett Saturnalia ünnepet. A saturnalia tragikus hősét sorshúzással – rendszerint kockadobással – választották ki. A kiválasztott életének utolsó heteit abban a tudatban töltötte, hogy a végzetes óra eljöveteléig ő az ünnepség királya, akinek mindenki engedelmességgel tartozik és mindent megkap, amit csak megkíván, de az ünnepség végeztével önkezével kell véget vetnie életének. Halálával lezárul a zűrzavar ideje és megszületik az új rend.
Bár konkrét nyomot nem találtam erre, feltételezésem szerint BC 153 előtt a római évkezdet március 1-ével lehetett, így az itáliai Kronosz (Saturnus, egyben parasztisten) tiszteletére a napéjegyenlőség előtt tartott ünnepségek a január 1-re tolt évkezdettel együtt eltolódott december második felére. Később a napév alapú naptárban a téli napfordulóhoz kötődött.
Etimologiai kísérletek
Prefix: The root word 'Sa'/'Saa' in Akan, Ancient Egyptian and Persian
In both Ancient Egyptian and Persian (Zoroastrian) traditions, the root word Sa/Saa is connected with wisdom. In the Ancient Egyptian tongue, one meaning for the word 'Saa' is 'wise man'. In Zoroastrianism, "asa" means truth or wisdom. A SA kígyót is jelent. Tán innét van a SA-tan szavunk. 26th Dynasty of Sa'ite Kings!
Fergus Sharman az egyiptomi és a bantu között is kapcsolódást lát. Például az egyiptomi MS (gyermek, utód > MS Rá-im?) etimonját a bantu SAA-ban találja. A KATI (woman/asszony) szó is előfordul mindkét relációban, de nem azonos a görög KATA (lehullott) vagy a wolof KATA (vagina) szóval. [Arawak "kathi=moon". Swahili "kati=middle".]
A "sa" kapcsán megemlítendő az egyiptomi napbárka, a SA-KHAR neve is. Vajon a SA és a NAP hasonló fogalmak? The s-collar read as Egyptian is the sa-collar, a symbol of wisdom, the sign of an order, or rank, or judgeship. Sa or us then is the tie, the sign of rank. ..s a TURN szó létezett már a korban és időben arra? ..s "köristenes" lehetett az Is-Sa-kar nemzetség? Issa al-masi! ..vagy a héber SA (ma SIN) az Holdat jelentett, Sahib? [hybla?]
SA az etruszkban állítólag 4-et jelent, a tru-na = power, rule. Akár négyes uralmat (tetr-archia) is jelenthetne a saturnalia, ha közel-keletiesre vesszük a figurát. De ez csak Diocletian idejével jött el.
ÓHebrew duma
sah, measure, a rabbinical measure, mystical.
thur, used of what goes or turns round in a circle,
turn, order, a turtle dove, the bird of return.
thur, physical purity opposed to impurity, to cleanse in the primal sense.
nah, shaking motion.
nah, to sit, to dwell, keep at home.
Juno
’Hra, ’Hrh, Juno, ősrégi görög-italiai holdistennő, Cronusnak és Rheának legidősb leánya (azért egyik melléknevén Saturnia) Oceanus és Tethys házában nevelkedett. Spartában [hol aigojagoV, «kecskeevő» volt a mellékneve, mert kecskét (aíx) áldoztak neki]. Érdekességként a kecske szlávos területeken KAZA, feltehetően a pásztora Kaza-ar. Az udmurt KECS változatait találjuk a turk népeknél. A kelta vidéken gabr, OHG ziga a kecske.
Érdekességként a Sicilian-Romanian fighhiu = fiu (fiú. Románok siculus eredete?) De nekünk Mohács kellett.. Arabs who conquered a Castle in Mudiqah in 845. The city yet changed its name to Motica, Motuca and Mohac. [Itt a Rahel nem juh, hanem falu jelentésű.] Szicilia: Ragusa is really two towns combined into one municipality: Lower Ragusa, known as Ragusa Ibla, which was the ancient city, rebuilt after the 1693 earthquake and Upper Ragusa, the new city built in the early 1700s on the ridge across from the old city of lbla after the earthquake. "Ibla" was populated by the indigenous Siculi in ancient times and was called "Hybla Heraea,". Modica az arab uralom után lett átnevezve Mohac-ra.
Bruma
The festival begins with a formal sacrifice at the temple of Saturn (whose name was derived from satus = sowing), which is conducted Graeco ritu (by Greek rite), that is, with uncovered head. First the woolen bonds are untied from the statue of Saturn. Next there is a festive banquet at which people dress informally, wearing the synthesis (perhaps a light dressing-gown) and pilei (soft caps), which may be made out of paper (Guhl & Koner 481). At the end of the banquet everyone shouts, "Io Saturnalia!"
Gyümölcslé
In the Saturnalia, Macrobius creates an imaginary symposium among pagan intellectuals in which he offers an explanation for the varying length of the holiday. Originally, it was celebrated on only one day, the fourteenth before the Kalends of January. With the Julian reform of the calendar, however, two days were added to December, and the Saturnalia was celebrated sixteen days before the Kalends (December 17), "with the result that, since the exact day was not commonly known?some observing the addition which Caesar had made to the calendar and others following the old usage?the festival came to be regarded as lasting for more days than one" (I.10.2). The original day now was given over to the Opalia, honoring Ops, who personified abundance and the fruits of the earth, and was the consort of Saturn. As the two deities represented the produce of the fields and orchards, so they also were thought to represent heaven and earth. It was for this reason, says Macrobius (I.10.20), that the two festivals were celebrated at the same time, the worshipers of Ops always sitting in prayer so that they touched the earth, mother of all.
Az idő folyását több nép a folyó vízzel hasonlította. Lásd szláv RIK és RIKA. Vagy a dán "är = év".
Winter Solstice
The 12 Days of Christmas -- The midwinter festival of the ancient Egyptians celebrated the birth of Horus - son of Isis (the divine mother-goddess). The celebration was 12 days long, reflecting their 12-month calendar. This concept took firm root in many other cultures. In 567 AD, Christians adopted it. Church leaders proclaimed the 12 days from December 25 to Epiphany as a sacred, festive season.
ORIGINS OF CHRISTMAS
Some of the major gods who celebrated their birthdays on December 25 were Marduk, Osiris, Horus, Isis, Mithras, Saturn, Sol, Apollo, Serapis, and Huitzilopochli.
During the end-of-year festivities, they recited their creation myth, then held military exercises symbolizing the great battle that was going on between the sun and the forces of darkness. Their surrogate king was crowned and accorded all the honors of royalty. But on the day of the solstice, both the surrogate king and an effigy of the god of darkness were burned in a huge bonfire.After the bonfire, the people exchanged gifts, held feasts, and visited friends and relatives. This was called the "Zagmuk" festival. The Persians and Babylonians held a similar celebration, which they called the "Sacaea."
Latin natalis, from nat- 'born', from the verb nasci. (Not Nasca!) Al-Nas.
Burushaski might be the mother language of Indo-Aryan and Indo-European, there are most of hidden words which are very much basic and there are words exist in Indo-Arian and Indo European languages in the shape of distortion like sa in Burushaski means sun, in ancient Indo-Arian the word for sun is Sa raj (sun’s upperness) which has been change into suraj where as in IE it has been changed into su’n, this page is very much short to explain how many words exists in such nature which can confuse one to think.
Sheol, meaning "grave, underworld," is of unknown etymology (Si-Ohl?), and does not appear to have a regular Hebrew root. It may be an Assyrian loan word, but this is disputed.
Sha'= See (note that the word for "ray/ sugár" in Arabic is Shu'a, derived from the Arabic verb asha' = to shine)
Pálfordulás
A damaszkuszi úton Saulusból Paulus lett. A saul nem keverendő a "shawl = sál" szóval. Általában a "saul=Nap" és a "pál=Hold" de van aki a saul szót kapcsolja a shoal=grave > hell (hellen, helikon, helios) szóval. De nem kizárt, hogy az örök hallgatás (shoa) az etimon.
Hebrew word for the sun is ‘Shemesh’ while Shamash was actually the winged sun god of the Sumerians and Babylonians, and these civilizations are far older.
Amikor meghal a Nap
Most stories about the origin of Halloween correctly state that Halloween had its origins among the ancient Celts and is based on their "Feast of Samhain." However, a writer in the 18th century incorrectly stated that Samhain was named after the Celtic "God of the Dead."
Hebrew gloss.
"sha-ar hash-shah-My-eem" The gate to heaven. "Shaba bath" meg a heti mosdás? Vagy hetedik ház?
Sámson és Delilah
The name Samson is the word shemesh (sun) suffixed with the “-on” (waw-nun) extension. This extension personifies or localizes the root: the name “Sams-on” means “Sun Man.” This, just as the name “Dag-on” means, “fish man.” A related Scriptural term is the place-name, “Beth-shemesh” (city of the sun).
Saturnalia
Saturn was known in antiquity as "the Star of the Sun" and in fact was considered to be the Sun -- especially when translated as "Sun Star."
Educ.
By the beginning of December, writes Columella, the farmer should have finished his autumn planting (De Re Rustica, III.14). Now, with the approach
of the winter solstice (December 25 in the Julian calendar), Saturnus, the god of seed and sowing (Latin satus) was honored with a festival.
Janus a portás
Modern scholars have conjectured that it derives from the Indo-European root meaning transitional movement (cf. Sanskrit “yana-” or Avestan “yah-”, likewise with Latin “i-” and Greek “ei-”.). Ianus would then be an action name expressing the idea of going, passing, formed on the root *ya- < *y-e?2- theme II of the root *ey- go from which eo, ??µ?. From Ianus derived ianua (“door”), and hence the English word “janitor” (Latin, ianitor).
Róma - Néprajzi viszonyok.
Saturnus kora az aranykorszak. Megszüntette a folytonos háborúkat és megteremtette a békés polgári életet. Felesége, Ops, a kivel örökre egybekelt, a gazdagság képviselője. A sarló, melyet a későbbi mythosok Saturnusnak, mint az Idő istenének, kezébe adnak, tulajdonkép inkább az a szerszám, a melylyel megtanítja az embereket fát nyesni, réteket kaszálni s a termést összegyűjteni.
A Saturnalia ünnepe, mikor később a rabszolgák egynéhány napon át a független polgárok összes szabadságait élvezték, emlékeztette a rómaiakat a közös jogok és a régi egyenlőség boldog korszakára.
A legrégibb valódi név Róma területén a siculusoké (szinte "sickle"). Dionysiosnak, a római régiségekre vonatkozó leghitelesebb adatok compilatorának szavai szerint «a várost, mely az összes országokon és tengereken uralkodik, s most a rómaiak birtoka, a siculusok telepítették be, egy a talajból fakadt népfaj.» A hagyomány szerint több várost alapítottak Róma szomszédságában, például Antemnaet, s bár kevés nyomot hagytak magok után, mégis azt hiszik róluk, hogy időről-időre Itália minden vidéke nyujtott nekik hazát. Erősebb népek fegyverei elhajtották őket a félsziget egyik végétől a másikig, míg végre Sicilia szigetén találtak állandó otthonra.
Valahogy nekem nem a mezőgazdaság ugrik be Szaturnusz és szerszáma, a sickle (Hold alakú sarló) valamint Ops asszony esetében. December második felében már a sarló pihen Itáliában is. A levegő opálos, párával szaturálódott. Mellesleg azt sem hiszem el, hogy a nagyurak helyet cseréltek a rabszolgáikkal, s az urak szolgáltak a jeles napokon.
Tudománytalan - de a fotók figyelemreméltóak
(Saturn/Satan). A szárnyas kecske-ember ördögi szarvval, fején a fáklyával (Lucifer a fényhozó szimbóluma), rajta a pentagrammával, karjaival mely mutatja "amint fent,úgy lent" (smaragd tábla) okkult jelszavát. És mint tudjuk... "nincs annál nagyobb rabszolga, mint az, aki tévesen szabadnak hiszi magát".
Mix
Vigilia
Kr.e. 23-ban - a nagy római tűz után - a császár megalapította 600 szolgával a tűzoltóságot, ami felváltotta a régi éjjeli őröket.
Oltár - a változás színhelye.
An ara is an altar, the structure on which a sacrifice is made. Arae were often open-air structures, immediately accessible to the public, whether within Rome or out elsewhere.
In descriptions of Roman sacrificial rites five different terms for designating the altars are commonly used: 1. focus 2. foculus 3. mensa 4. ara, and 5. altaria. Az oltárok között feltűnik a palesztinai típus, sarkain szarvakkal.
Erfurt The sponsor of the altar, Mucronia Marcia, also dedicated a sacred grove (lucus). A római jogú városok a kolóniák voltak. Nézetem szerint a "kolonia" a KOLO, korábban a HOLD(kör) szóra vezethető vissza.
Szardinia
Sardinia - Nurage
There are over 7000 examples spread all over Sardinia, characterised by truncated-conic towers with a circular internal room covered by a tholos or false dome (nur is a preindoeuropean word that means "hollow heap"). Nuraghe
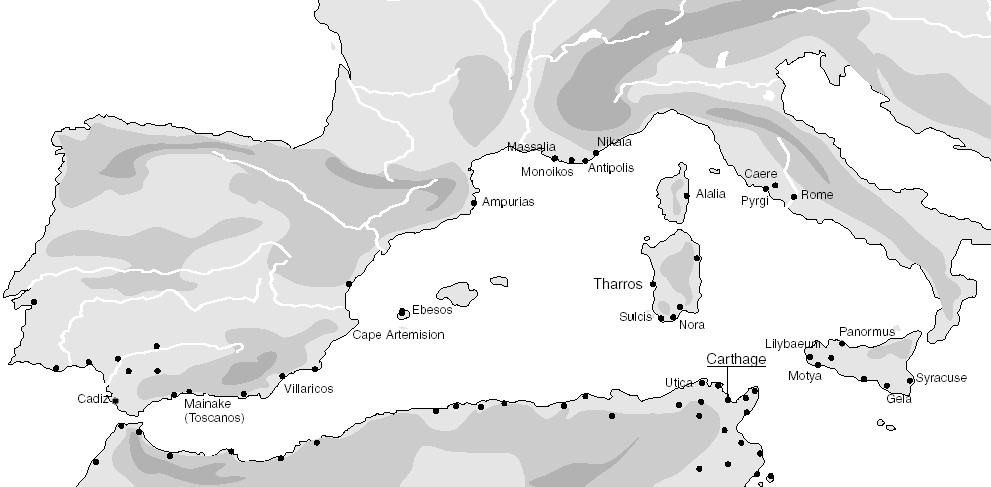 It was in this area that the first Phoenician colony, Kition, was founded around 820 BC. In Sardinia, the famous ‘Nora stele’ with a Phoenician dedicatory
inscription conventionally dated to the 9th century BC also belongs to this group.
It was in this area that the first Phoenician colony, Kition, was founded around 820 BC. In Sardinia, the famous ‘Nora stele’ with a Phoenician dedicatory
inscription conventionally dated to the 9th century BC also belongs to this group.
Szárdok
A vulgáris latin különleges, szardiniai fejlődésében, azaz a szárd kialakulásában szerepet játszottak az őslakók által beszélt nyelvek is (ezekről sajnos csak nagyon keveset tudunk). Miközben a latin egyre nagyobb teret hódított, s szorította ki az ősi nyelveket a használatból, ezekből szükségszerűen átvett elemeket, s ezzel maga is változott. A "latin" kor után, az 5. században jöttek a gót és a vandál hódítók, századokkal később az aragóniai uralom (spanyol és katalán hatás), amik más nyelveket hozva a szigetre, különböző mértékben, szintén "irányították" a szárd változásait.
Nyárutó
If Nurae, Nurra, Nur-ake have the same base, what is the origo prima? It regards to the Akkadian term nuru(m) 'light (of the sun)', numru 'glow, splendor (of the sun, of god)' referred to the highest concept of the sacred, to the 'light', then to eternal fire that glowed in the night on the top of all ziqqurats, on ziqqurath of Monte Accoddi, on the summit of the hills in the shape of ziqqurath, on Mount Timidone that arises tall and venerable over the foams of the coast of Alghero. In Aramaic and Ugaritic Nur is the 'Goddess of Light', 'that enlightens'.
Sumerian nu 'creator', '(divine) semen' + ra 'pure','shining' (see Egyptian Ra 'shining sun'),
Jósda
A Szibilla név eredete nem teljesen ismert. Úgy véljük, görög eredetű szó, s Apollo isten jóstehetségű papnői voltak a szibillák. Mindenesetre a BILA(g) az arabok felé "ország" (felénk világ). Esetleg megemlíthető a billog szavunk is, amely egyik jelentésében KÖR. De mit jelenthet a SY ?
Nem a sötétség terjed, csak a fáklyák fogynak..
Sybilla Cumana 9 jóskönyve
A klasszikus latin írok szerint a küméi Szibilla kilenc könyvben írta le jóslatait, és ezeket óriási összegért ajánlotta fel Plinius szerint Trquinius Superbusnak, az utolsó római királynak (i.e.534-510) Amikor az uralkodó visszautasította, a Szibülla három könyvet tűzbe vetett, majd a maradék hatot ismét megvételre ajánlotta úgyan annyiért mint az előbb a kilencet. Az újabb visszautasításra megint elégetett hármat; végül elérte, hogy a maradék háromért megkapta az eredeti árat. Ezeket a könyveket a Capitoliumon, Jupiter templomában őrizték, kezdetben 2, majd 10, később 15 tagú papi testület felügyelete alatt.
Könyvégetés
Ha megnézzük az 1572. évi Tycho-féle csillagokról szóló egykorú irodalmat, illetve a hasonló témáról értekező 16—17. századi nyomtatványokat, sok helyen találkozunk az ú.n. Szibilla-jóslatokkal. Az eredeti római jóslatokat nem ismerjük, mert azokat i.sz. 405-ben Stilicho parancsára elégették.
Antiszemita
Ezeknek a kitalálásoknak legjelentosebbike Szibilla jóslatai voltak, Alexandriai zsidók hamisítványai, amely egy Isten uralmának eljövetelét jósolták meg. De utánzóik is lettek, mert mióta Szibilla elkezdett beszélni, kétszáz évvel Krisztus eljövetele elott, az elso keresztények is megszólaltatták. A zsidók eltulajdonították a görög irodalmat és filozófiát is.
Hitélet
A Szibilla orákulumok vagy jóslatok, bizonyos ősi pogány és "keresztény" jövendölések különös gyűjteménye. Az eredeti szibillákat (jósnőket) maga "Apollón szállta meg", akik ennek hatása alatt jelentették ki jövendöléseiket. A kereszténység megjelenésével nagyszámú keresztény szibilla jóslat is elterjedt. Érdekes módon, az ún. cumaeai szibillákban Apollón és a Messiás nevének azonos számértéke van, ez a szám a görög betűk számértéke szerint 888
Etrusk
Vergiliust, a költő-történészt például a jóslások drámai lefolyása ragadta meg: „A sziklába óriási üreget vájtak (…). A küszöbre érve már kiáltott a szibilla: Kérd az igét. Gyorsan. Az isten, oh lásd az isten. És miközben a bejáratnál ezeket kiáltja, hirtelen megváltozik arckifejezése és színe, lebomlik a haja, zihál a mellkasa, vad őrület járja át szívét, és hangja nem emberi többé”.
Etrusk
Etruszk szószedet
celu priestly title [g/lb83, mp68]. cep-, cepen, cipen, cepen-e, cep-ta, cep-ar priestly title [g/lb83, mp68] rector, president, head" [az96]
Cale clante "a gall örökség"
Calu, calus Pokoli démon halál istene "Sötét, sötétség"
calusin, calusna "vonatkozó Calu" "Sötétedni, gyászos". calusna "sötét"
cap- "tegyék, hogy tartalmazza"
köpeny, CAPI, kape, Kapi, Cape-r, Cape-ri "ivóedénybe, konténer"
caperi (gerundium Cape) "kap, fogd"
caperxva "tartalmazó (mn.)" [MP68]
Capra "konténer, urna, temetési urnát"
* Capr-, * capre "April"
carcu, carcuna, carcna, carcusa, karke, karkana, karxvanie "őr, megfigyelő" [az96]
Carcer "börtön" Latin etruszk eredetű [rc 74]
Cardo "észak-déli tengely templomban" [MP68: 250]
Caru "van / részt venni, hívd" [az96]
caSni, cazni "éles, vágás" [az96]
caspre "éles" [az96]
|
catena "lánc" Latin etruszk eredetű [bm 24-25]
Cath, cathin "megragadni, felfogni" [az96]
Catha "rab, elfog, vadászat, háború" [az96]
catharnai "istennő megérteni, elfog, vadászat" [az96]
Cathe "okos, intelligens, ravasz" [az96]
CATU "háború" [az96]
caz- <* kast- <* kwedh-t "éles, hegyes" [az március 29 99]
ceizra, xaire, xeri, xaisrie, cisra "Cerveteri (város)" [az96, DJH 14, g / lb83]
celsclan "Son of Cel (sun istennő)" [g / lb83]
cele "nőtt, a nagy, magas" [az96]
celthi "mellnagyobbítás, ünneplés" [az96]
<* Kel-, * kil- "nő" [az96]
Cela "szoba" [az96, g / lb83, mc91: 99]
Celi "szeptember" [g / lb83, MP68] lásd Latinized Caelius, Celius [g / lb83, MP68]
|
PupLuna - Etrusk
The Roman city of Populonia was originally named Pupluna, probably after the Etruscan wine god, Fufluns. It was situated on the western coast of central Italy near present day PortoFerraio, on the Monte Massoncello Peninsula--the only large Etruscan city directly on the sea. Testvérvárosa Pamplona? A település nevét eredeztetik az etruszk Bacchus "Phuphluna" nevéből, bár néhol "Puplana" név látható. Ez volt az etruszkok egyetlen tengerparti kikötővárosa állítólag. (Port of Volterra). [A "pup/pap" némelyik nyelvben "mell", vagyis nő. A pupluna akár holdleány is lehet.]
Crawford: Etruscan inscriptions analysed
We have also the wild boar; and a coin with a female head covered with the lion's skin, and a club on the reverse, which evidently points to Hercules, the female head being identified by Miiller with that of Omphale, although he suggests a doubt whether it may not be that of Hercules in youth.
The wild boar, 'aper, cq)Jiul " the animal that peculiarly strikes, may, in the stage of the digamma, have been used as a symbol of pupl- in pupluna. That 'Omphale,' with the digamma, equally answers to pupl- is evident; but the same connection exists with Hercules also through his symbolical tree, the * populus,' and the primitive afl, Fafl.
Populonia
The only Etruscan city of any size on the Mare Tyrrhenum (Str. 5,2,5; Plin. HN 3,51), facing Elba, 14 km to the north of Piombino with a good natural harbour in the modern bay of Baratti.
Etrusk
Fig. 4. On the left, saffron-gatherer from Room 3a, Xeste 3, Thera. On the right, girl dancing with incence burner on her head from the Tomb of the Jugglers, Tar-quin-ia, 6th century BCE. Mások írták: Capua derives from "hawk", which is pronounced in Tuscany as "Capi". Megint másoknál a "capi-s-trum" egy csapda, görög eredetű kelepce.
Etrusk origin
Let’s take Mario Alinei for example. His idea that the Etruscans descended from ancient Hungarians is based on archaeological and linguistic evidence. Maybe he's right, or maybe not, but in any case his proposals are coherent. The Italian to this day call a Germán, Todosco.
Tuscan archipelago. A 7 sziget legnagyobbika Elba. Het-rus-can..:-). Sevillai Isidor szerint a vallásos rítus (tus) után kapta nevét Tus-ci. Az etruszkba Emiliából érkezett szó az "umbricus", ami "köldök" jelentésű. A cseheknél a rit(us) az anus. A cere-monia pedig számos nyelven ritus.
etrusk
Apart from this unusual storyline, this mirror is significant because it confirms the name of the consort of Tinia in mirror Divine_Mirror.html, Script DM, THALNA, her name probably derived from "retaliation" (L. talio-onis, f). Megtorlás, bosszú. [A "tolna" szót említették már az etruszk "ifjúság istennőjé"-nek, de rokonítható a "Hold, tűz, út" szavakkal is.]
Ligur
Triglav - Galiciaiak
Lugus was a deity of the Celtic pantheon. His name is rarely directly attested in
inscriptions, but his importance can be inferred from placenames and ethnonyms, and his nature and attributes are deduced from the distinctive iconography of Gallo-Roman inscriptions to Mercury
Lug
The iconography of Gaulish Mercury includes birds, particularly ravens and the cock, now the emblem of France; horses; the tree of life; dogs or wolves; a pair of snakes (cf Hermes's Caduceus);
Pseudo-Plutarch in fact suggested that the city of Lugdunum was named after the ravens, stating that "lougon ton koraka kalousi" (they [the Gauls] call the raven 'lougos').
Lugus/Lúgh is associated with the festival of the first of
August. This festival was called Lughnasadh (Literally 'The Marriage of Lugh') in Ireland and when the Emperor Augustus inaugurated Lugdunum as the capital of the Roman Gaul in 18 BC, he did so with a ceremony on 1 August.
Enlil és a légurok: Lugus kelta isten neve városnévként a Fülöp-szigeteken, Sulu tartományban is megtalálható. Ez az ugandaiaknál összevontan Lugusulu-ként tűnik fel.
lug·worm= any burrowing annelid of the genus Arenicola, of ocean shores, having tufted gills: used as bait for fishing.
lug·sail = noun Nautical a quadrilateral sail bent upon a yard that crosses the mast obliquely.
Lugo = town, Emilia-Romagna regione, northern Italy, just west of Ravenna.
Lugos = város a Temes partján
lughole = ( Brit ) an informal word for ear See also lug
Csillagember
There is a bit of silicon stone from Arguel in France with ARBITAG WODAN LUGODHA ZEJ? KIM? The root ARBI in Gothic means "heritage". But Wodan is clear and
LUGODHA is known from Celtic times as the god Lug with many synonyms and the name occurs even in South Sweden.
Liguria neveiből - fura etimológia
Name: Tavia fl. (It. Mar.) [Nem "tavon át" ill. vizi út.]
Etymology: The hydronym has two exact counteparts like Tava fl. (Britannia), which likely derive from the IE root *teu- 'to swll, crowd, folk, fat, strong, boil, abscess'. Also the Ligurian name could therefore be Celtic in origin.
Place: river Tanaro, region Piemonte, Italy
Name: Tanarus fl. (Plin., Paul. Diac.)
Etymology: According to Pokorny, the hydronym derives from the IE root *(s)ten- 'to groan', from the sound of the water.
ligarius
Scoglio La Cassa ("scoglio" means "rock" in Italian > sasso, rocco)
Diocese
A katolikus egyház megyei szervezete. Nem feltétlen azonos a világi megyével a területe. Élén a püspök (episkopos=felügyelő) áll.
Káptalan
Spanish Verb
ceses: Informal second-person singular (tú) present subjunctive form of cesar.
Latin Verb
cessare: present active infinitive of cesso
Nathan Bailey: CE'RUSE: white lead (Latin cerussa)
To CESE: seize, Chauc.
Diocletian korával: Administrative division of the later Roman Empire, starting with the tetrarchy.
Diocese
On the other hand, the present meaning of the word diocese< is met with in Africa at the end of the fourth century (cc. 50, 51, C. XVI, qu. 1), and afterwards in Spain, where the term parochia, occurring in the ninth canon of the Council of Antioch, held in 341, was translated by "diocese" (c. 2, C. IX, qu. 3). See also the ninth canon of the Synod of Toledo, in 589 (Hefele, ad h. an. and c. 6, C. X, qu. 3). This usage finally became general in the West, though diocese was sometimes used to indicate parishes in the present sense of the word (see PARISH). In Gaul, the words terminus, territorium, civitas, pagus, are also met with.
Par-ish „A plébánia (latinul: parochia) a krisztushívőknek a részegyházon belül tartós jelleggel alapított közössége, melynek lelkipásztori gondozását a megyés püspök felügyelete alatt egy plébánosra bízták, aki annak saját pásztora”. A parokia a görög "par-oikos" átvétele. (Oikos = vicus = ház) "para=near"
Roman art a trón. Háttámláján kígyóval. Csak nem Mac Edon fiai? Apollo trónja
Underground - Mithrász kultusz
This religion’s main places of worship were mostly hidden and underground. They are called Mithraea, buildings dedicated to a deity associated to a solar dimension, protector of justice, and linked to salvation and that in many respects, as we shall see, with resemblance to the figure of Christ.
Diakónus
Az első századok keresztényei a római birodalom társadalmának ellenséges környezetében törekedtek Krisztus követésére, illetve vallották meg a Megváltóba vetett hitüket az üldöző hatóságok előtt. A keresztények üldözése azonban nem terjedt ki általánosan az egész birodalomra, s szigora és mértéke a helyi hatóságok, a helytartók buzgóságától függött. Ifjabb Plinius, Bythinia tartomány kormányzója is társadalmi nyomásra keresztényeket végeztetett
ki. Eljárásának helyessége és jogszerűsége iránti bizonytalanságában fordult Trajanus császárhoz irányelvekért, mivel ő nem igen talált a keresztények között bűnöst, noha még azzal is megpróbálkozott, hogy „...két szolgálóleányból – ezeket ők diakonisszáknak nevezik – még kínvallatás árán is kivegyem az igazságot. Nem találtam bennük egyebet ostoba, határtalan babonaságnál”.
Post coitus omne animal triste.
Cunt és a latin sex
ISIS- Sham Sulla .-:)
(Sham being an Arabic term that refers to Greater Syria). Barack Obama átnevezte az ISIS-t (Sham iszlám állama) ISIL-re (Levant iszlám állama) névre.
Italic-languages
A bruttiumi bronzasztalon Bantia település törvénye olvasható archaikus latin nyelven, ahogy írják.. magyarul
siculo coin: Panormos (c.340-320 BC)
Érmék: Az egyik oldalon Tanít istennővel, másik oldalon egy lóval.
Karom
Not so with Libra: to the ancient Romans, Libra represented scales, to the ancient Hellenes, the claws of the constellation Scorpio. As such, it was known by two names: Zyygos (the Scales) or Khêlai (the Claws).
Assinarica
Porte Asinorum? (Asinus: ismeretlen eredetű a latinban) Magyar írásokban erről a kapuról nem találtam információt. Tán attól féltek a finnugorászok, hogy a magyarok nem a szamárra vagy a hátsó fertályra asszociálnak a névről. Mert ugye, lehet ezt tagolni As-sin-ar-ica formában is. Ami jobban passzol a Cael-ián dombhoz vagy a Pal-atin-ushoz.
Gates
Az Aurelian császár építtette fal egyik kapuja volt az Assinarica kapu, amelyen át Tusculanum felé lehetett menni. Asina-rica: A "rico" jelentése lehet "sexy, hot". (+ nemes, gazdag, szép, ízletes, válogatott). Vicus Tusci, utcza Rómában, rosz emberek, küln. kéjhölgyek tartózkodó helye. (lanus, mn.; küln. fn. a) ani, orum, hn. t. T. lakosai. Finaly Henrik szótára)
Az "Asinarica" egy keskeny kapu volt, amit többek szerint a szamarak számára építettek, amiket ezen át hajtottak be a Caelián és a Palatinus dombok mellett. (Porta Asini latinul. De Jókai egyik hőse (Lándory) is tiltakozott, amikor a franciák L'ane d'Ore-ként ejtették nevét.) Annyi igazság lehet a dologban, hogy néha szamarak hajtották a malmokat, de nem hinném, hogy ezek a malmok Róma legelőkelőbb részén lettek volna.
Vatikán
Vatican City and St. Peter's Basilica of the Roman Catholic Church were built upon what was called in Latin vaticanus mons or vaticanus collis. The words mons and collis mean hill or mountain. You will also find in the dictionaries that the words vatic / vates / vatis all relate to prophecy.
Assinarica út vezetett a Lateranból a Caelian hill-re? Hungarian "assoñ = woman". In Hindi the meaning of the name Kanya is: Virgin, "young woman" in Thai. Heya is Girl/Female and origin is French, Indian, Russian; Heya means: Sweet. Greek name, Antheya means "flowery". It's possible that the phrase bat heya'na solely denoted some kind of vulture (there are sixteen Old World species alive today and an untold number of extinct ones), but the descriptions outside the Torah are too fitting to hyena's to disregard. Arabic: "She = heya".
Assisi Kánya vagy héja? [Szláv hangutánzó szavak :-).]
The Romans called it "Asisium" and "Asis" (Propertius [50-15 BC]).
"Asisium" could come from the mountain "Asio", as Bruschelli thought, or from the “Assino” River.
Recently a third option was proposed, that, as we saw, now enjoys considerable consideration. According to this hypothesis, "Assisi" means "the city of ‘astore’ [meaning "hawk" or "bird of prey"]. Catalan astor=goshawk/héja. Greek: eídos gerakíou. Magyar: vándor sólyom. Vietnamese: Ung lón. Spanyol: Halcón Peregrino. Észt: Rabapistrik. Baszk: Halkoia, "Aztoria=héja". Galego: azor=héja. Albán: gjera-gina=héja (Kanya?). Finn: Kana-haukka=héja. Észt: Kana-kull=héja. Occitan: "astor=héja". Romani: "hulyo=héja".
Kite = Kánya. Macedonian: lunja. Mazanderani: jul. Occitan: milan. Latin: miluus. Polish: kania. Slovak: haja. Venetian: poja. Mandarin: yuän. Armenian: urur. Albanian: qift. Nivkh (Outer Manchuria): p'isk. [Akkor Bishkek nem püspök?]
Umbria
The name Umbria is derived from the Umbri, one of the chief constituent stocks of the Italian nation. The origin and ethnic affinities of the Umbrians are still in some degree a matter of dispute, but their language proves them to have been an Aryan people closely allied with the Oscans and in a remoter degree with the Latins.
Umbrians were cognate with the Achaeans of prehistoric Greece. Pliny's statement (III.13, 19) that they were the most ancient race of Italy.
Asisium
Place: Assisi, province Perugia, region Marche, Italy
Name: Asisium (Plin., Prop.) Aesisium (Ptol.)
Etymology: The name has been explained as as-isium 'town of the hawk', like Brundisium is the 'town of the deer', or from a stem *assa 'stream' (UTET).
Asi
The town of Assisi (Assisium), which takes its name from Mount Asi, on which it is situated, lies almost in the centre of the province of Umbria, about halfway between the cities of Perugia and Foligno, and forty-one miles north of Rome.
Ancient Rome
In the Iron Age, an archaic city emerged on the left bank of the river enclosing the four regions: Suburana (Caelius), Esquilina, Collina (Quirinal and Viminal), and Palatina. The Capitoline, always regarded as the citadel of the united city, was not included in one of the regions. The archaeological evidence of Iron Age tombs and hut foundations is, however, not limited to the Palatine, Quirinal, Esquiline, and Velia; it also appears to a large extent in the valley of the later Forum Romanum although the legend describes this as a marsh made habitable only by the draining by the Cloaca Maxima, attributed to the engineering skill of the Etruscans.
Laterano
The present Piazza di San Giovanni in Laterano was an important road junction in ancient times. It is suggested (with some debate) that before the Aurelian Walls were erected the ancient main road of the Via Tusculana ran up the west side of the present basilical complex and along the present Via dei Santi Quattro Coronati. This route was provided with a postern gate where the ancient city wall does a zig-zag, but traffic then mainly used the Porta Asinaria. The importance of this road is that the baptistery preserves the alignment in its major axis.
Assen:
Assenarica - Róma kapui
The eighth is the Porta S. Johannis, which by the ancients was called Assenarica (Asinaria). Latinul: ** Octava porta Sancti Johannis, quai apud antiquos Assenarica dicitur.
Assen települések a világban. Zömük feltehetően holland eredetű, bár Bulgária esetén ez tán kizárható. Meg a portugál Assen-tiz is inkább afrikainak tűnik. (Tiz=Hold.) Egyes etimológusok szerint a "Porta Asinaria" jelentése Szamárkapu. Donkey's Gate [Donkey gate is a gate in the Aurelian Walls of Rome, constructed in 270-273 AD to the South-West from the Gate San Giovanni]. A kaput az Asinaria út végén építették. Szamaraknak: 535 Belisarius entered Rome by the Porta Asinaria. Medical, porta of lung ( hilum pulmonis). Az Asenarica kapu mögött terült el Lat-eran.
Assen: az angoloknál nőstény szamár. Albán szamár: magar. [Segg/Ass: Persian: kun. Arab: tiz.] Asen and his family were Vlakhs.
Asinara: It is home to a population of wild Albino donkeys from which the island may take its name.
A sil fiai
In other words, the first issue of these later " medallions/* with the prize trophy beneath the racing chariot, connects itself in the most natural way
with the New Games instituted at Syracuse to commemorate the " crowning mercy " of the Assinaros.
With these figures on coins of Cyrene may also be compared a figure with wings at shoulders and ankles, and apparently holding a silphium flower [the ancient Greeks as a food and medicine], on a fragment of a situla found at Daphnae in Egypt (Petrie, Tanis, Pt. II., Nebesheh and Defenneh, PL XXVI. 4), which probably also represents a harpy or wind-diemon, though Mr. Murray, in his chapter on the Daphnae vases in Mr. Petrie' s work (p. 67), has called it Nike. Silphium: A botanical-horticultural riddle: what is the plant the Romans called laser, laserpitium, or silphium, the English laserwort or magydare, the Arabs asa (hence asafoetida), and the Indians hing? Answer: a plant that might be lost forever and the Greeks called it silphion. It would appear that the word asa, (assa, aasa) is the Arabised version of laser the Roman word for silphion. (Thapsia was sold in 19th century Paris, for pulmonary afflictions, as silphion cyrenaicum!) The Arabs have very early confused the nature of the two plants and called both thapsia and silphion drias, or adrias which might be a misheard version of magydaris.
7 halom
Caelian: Mons/Collis Caelius
Many of Rome's elite lived on this hill during the Roman Republic.
Augur
Claudius Centumalus: an apartment house (insula) on the Caelian, which the owner was ordered to demolish because its height interfered with the observations of the augurs. Citadella: The Arx is also thought to be the site of an open air "templum" where augurs watched the activities of birds to see if it was safe to undertake proposed actions.
Seven Hill - Róma
The Caelian Hill is the southernmost of the four large spurs. It stretches from the area of San Giovanni in Laterano to the Colosseum. It had two high points, referred to as the Larger Caelian (Caelius maior), to the west, and the Smaller Caelian (Caelius minor), to the north. Servian wall: Porta Querquetulana nyílik Tusculanum felé. (Cicero és más előkelőségek nyaralóhelye, pl ahol a szeretőiket tartották.)
Querquetulana: A tölgy/querqus nevét a kelta "Quer = szép" és cuez = fa? szavakból eredeztetik. [Nem Kör-kus] A Szentírásban a tölgy nevei (éláh, ‘alláh, ‘élon, ‘allón, ‘éil, ‘él) ált. nagy, idős és szép fára utalnak. Isten nevét rejtik (‘Él ), Jupiter fája, kivágni tilos. Keleten Pál isten fája. (pälit)
Írják, hogy Róma alapítása idejéig "szent tölgy liget" fedte a Caelian dombot, amelyet aztán az etruszk Caile Vipina megtelepedés után neveztek volna el Caelian (Égi) dombnak. Majd kétszáz évvel később a Servian fal (murus Servii Tullii) kapuját még mindig a liget után nevezik el.. Tölgyesen túli kapunak.. Vagy a "szép sor utáni kapu"-nak.
Irish Gaelic: "the tree = an crann". Alder = éger fa, Gaelic: Fearna. Fir, (Scotch).—Latin, Pinus sylvestris— Gaelic, Giutha?.— The. Scotch Eir. Oak.—Latin, Quercus robar—Gaelic, Darach.
Fa: Across time and cultures, there were many words for tree ranging from "dru" or "daru" in Sanskrit, "tre" in Icelandic, "trae" in Danish, "trad" in Swedish, "drevo" in Russian, and "dpus" in Greek. In Welsh a word for trees was "gwydd" which meant a flexible twig. "Ptorthus" is classical Greek for a tree sapling, while "dendron" signified a tree. Barbary Macaque. A Proto-Italic *kwerkus lehet a "vértölgy" etimonja. Portugál: O que quer = Mit akar? Mouros, ja de quantos quer que fossem gan hava almas.. Quen quer que na virgen fia is, as a result, a dreadful mess. Iguan: Phymaturus querque. Latin: Queror = complain, lament.
Assinia
The Asinii came from Teate, the chief town of the Marrucini, and their name is derived from asina, which was a cognomen of the Scipios, as asellus was of the Annii and Claudii. The principal cognomina of the Asinii are Agrippa, Celer, Dento, Gallus, Pollio, and Saloninus. (Oroszok "z"-vel írják: Azi-nii.)
Sziciliai vereség - Magyarul ez
The Athenians pushed on to the Assinarus river, all the while being devastated by the spears, arrows and stones coming from everywhere and by the hordes of cavalry and other troops. They thought that if they could just get across the river, things would be a little easier for them. They were desperate to stop the pain, to drink some water. When they got to the river, they broke ranks and ran into it, every man struggling to make the brutal crossing first as the enemy bore down. Driven to cross all together, they fell onto one another and trampled each other down. Some were killed immediately by their own spears; others got tangled up in their equipment and with each other and sank into the river. Syracusans positioned on the other bank, which was steep, hurled down spears at the Athenians, most of whom were jumbled together ravenously drinking from the nearly dry riverbed. The Peloponnesians went down into the river after them and did most of the killing there; and though it quickly became fouled, the Athenians nonetheless fought among themselves to gulp the muddy water clotted with blood.
Sicani way: the river Helorus could also have had the name of Assinarus ? Sy-Cilia map
Syracuse ellen
The Athenian fleet first sailed to Corcyra to meet up with their allies, and the ships were divided into three sections, one for each commander. Three of the ships were sent ahead to look for allies in Sicily. The fleet at this point consisted of 134 triremes (100 of which were from Athens), 5100 hoplites (2200 Athenians), 480 archers, 700 slingers, 120 other light troops, and 30 cavalry, as well as 130 other supply ships and all the crews of the triremes and other non-combatants.
Mongol invasion
Anticipating the break of the defenses, King Louis kept his bodyguards and knights mounted, in order to quickly respond to the breaches. And those were not late to appear. The Mongols overwhelm the defenses in several points and the gate Porta Salaria (situated in the North-Eastern side) was stormed and opened. The Mongol cavalry purred through the gate, but they were stopped by a charge of heavy knights near the Colina square. Shiban, which personally lead the assault, was killed by a mace blow. However, Louis was forced to retreat his troops as the south-eastern gate of Porta Assinaria, also fall. The Lateran palace and the Basilica were utterly sacked by the Mongols.
Lat-er-an. Mondjuk, a Lateran származhat a görögök "imádat" szavából is.. vagy fordítva.
Greek
In fact Greek settlement in southern Italy and Sicily had created dozens of cities whose total wealth and population challenged that of mainland Greece. Greek cities such as Corinth, Athens and Sparta sent out colonies all over the Mediterranean world during the 8-6th B.C.E. centuries, and found in southern Italy and Sicily a land so vast and rich that they called it Magna Graecia, ‘Greater Greece’. The Romans readily overcame colonies such as Cumae and Neapolis, but in the late third century was involved in a vigorous war with Tarentum and her allies, which drew in the Molossian King Pyrrhus from Elis, a powerful city in north-western mainland Greece. Pyrrhus drew on the military methods of the Macedonians and also included elephants in his forces, making him a formidable foe (Delbrück 1975, p297).
Tyrseniann
(Tyrsenisch, also Tyrrhenian), named after the Tyrrhenians (Ancient Greek: Tursànoi, Tursènoi, Turrhènoi), is an extinct family of closely related ancient languages proposed by Helmut Rix (1998), that consists of the Etruscan language of central Italy, the Raetic language of the Alps, and the Lemnian language of the Aegean Sea. Rix assumes a date for Proto-Tyrsenian of roughly 1000 BC
Csap-víz
in Calabria we have historically ad fluvium Sabutum (Codices Sabbatum) = Savuto Itin. Ant. 105,5/ 110,8; Anon.Rav.386 Crater, Cratia = Sabatum.
ancient Sabis = Belgium. Oscan, Latin sapa juice /greek opos. aphia/.
Vizi világ - Orchipelago
As regards its further derivatives, we have OE īġoþ ‘islet, small island’ (hence modern ait ~ eyot, used mostly with reference to the topography of the Thames). Finally, Germanic *ēɣ⁽ʷ⁾ijaz
(cf. the ON ocean-giant Ægir, OE ǣġ(e) ‘island, sea, sea-coast’). Tocharian A yok- ‘drink’ .
3 pont - Hackenkreuz
The swastika has been found around the world and some of its earliest versions include branches, where the design grew from a symbol of trees to geometric form, of simple bars with buds on them, as seen in the ceremonial bowls from tell Baghouz, Syria (Samarra culture 5500- 4800 B.C.).
A 3 pont feltűnik a mükénéi civilizáció szimbólumai között, a Torello múzeum egyik lándzsafején, Schliemann egyik aranykorongján, egy villanovai kunyhó-urnán vagy egy etruszk tükrön (Szemelé Dionysus anyja).
Etymology
•• Il toponimo a. *Excingomagus (o *Escingomagus) va interpretato come ‘campo’ o ‘mercato di *Excingos’, essendo composto da un NP gall. *Ex-cingos ‘l’attaccante’ (‘che parte per attaccare’ < *cing- ‘andare, avanzare’ [vándor?]) e dal tema -mago- [mágus] ‘campo’ [terület] (poi ‘mercato’). Cfr. i personali Ex-cingus, Es-cingo, Ex-cingo-marus, e il toponimo Rigomagus.
Aki sosem látott hunt
Ammianus Marcellinus
Thus the Halani (whose various people it is unnecessary now to enumerate) are divided between the two24 parts of the earth, but although widely separated from each other and roaming over vast tracts, as Nomads do, yet in the course of time they have united under one name, and are, for short, all called Halani because of the similarity in their customs, their savage mode of life, and their weapons.
Itt is elhangzik az az őrület, hogy a Halani és a Hun szövetség megveri a gótokat a Tanaisnál. Ezek után a tönkrevert gót sereg nekimegy a rómaiaknak, akiktől veretlenül még félt. Mint amikor Árpád apánkat az gaz besenyők átkergetik Vereczke híres útján, s elkeseredésében Árpád népe letarolja Európát. Valahogy régen bármit be lehetett adni a népnek...
History
This race of untamed men, without encumbrances, aflame with an inhuman desire for plundering others' property, made their violent way amid the rapine and slaughter of the neighbouring peoples as far as the Halani, once known as the Massagetae.
Thus the Halani (whose various people it is unnecessary now to enumerate) are divided between the two24 parts of the earth, but although widely separated from each other and roaming over vast tracts, as Nomads do, yet in the course of time they have united under one name, and are, for short, all called Halani because of the similarity in their customs, their savage mode of life, and their weapons.
In all respects they are somewhat like the Huns, but in their manner of life and their habits they are less savage.
Latin atr- is the prefix meaning black and gula in Latin means throat.
Perzsia kontra Róma: Singara is besieged by Sapor, and captured. Pedig a Tigrisen inneni várost 2 légió védte: Az első Flavian és az első Parthian.
Persze, egy jó mesében valós elemeknek is kell lenni, különben csak az oviban figyelnek rá. Valóban jött keletről a massagéta (Mah-Saka-Ta) nép, amelynek neve Holdvándor-ként fordítható. A Hold meg szinte Halani.
Pesti István 2017 március
Nyitólap
 It was in this area that the first Phoenician colony, Kition, was founded around 820 BC. In Sardinia, the famous ‘Nora stele’ with a Phoenician dedicatory
inscription conventionally dated to the 9th century BC also belongs to this group.
It was in this area that the first Phoenician colony, Kition, was founded around 820 BC. In Sardinia, the famous ‘Nora stele’ with a Phoenician dedicatory
inscription conventionally dated to the 9th century BC also belongs to this group.